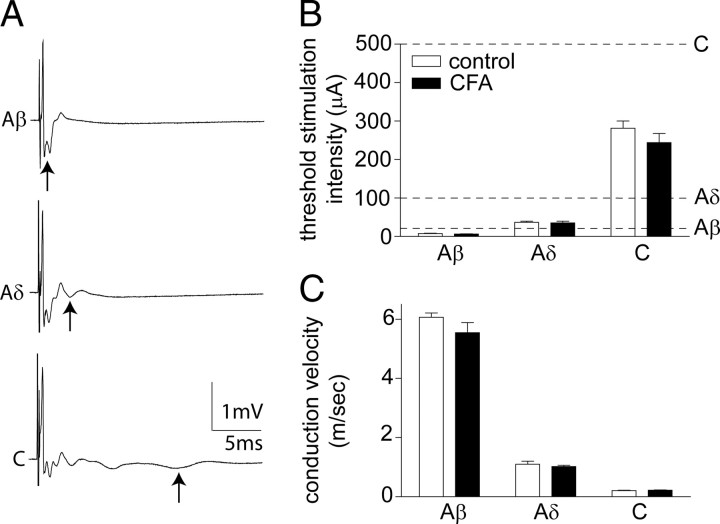
Figure 2.
CFA inflammation does not alter primary afferent thresholds or conduction velocities. A, Representative compound action potentials recorded from an isolated dorsal root, from a naive rat, illustrating the fast (Aα/β), medium (Aδ), and slow (C) conducting components evoked by 25, 100, and 500 μA stimulation in the top, middle, and bottom panels, respectively (average of 10 traces shown). Arrows denote the negative component of each triphasic (positive–negative–positive) afferent profile. B, C, Effect of CFA inflammation on the threshold stimulation intensity (B) and conduction velocity (C) of the different afferent components. Averaged data are represented as mean ± SE. Dotted lines in B indicate the dorsal root stimulation intensities (Aβ, 25 μA; Aδ, 100 μA; C, 500 μA) used in the subsequent patch-clamp electrophysiology studies. Two-way ANOVA reveals no significant effect of CFA inflammation. n = 8 in both groups.