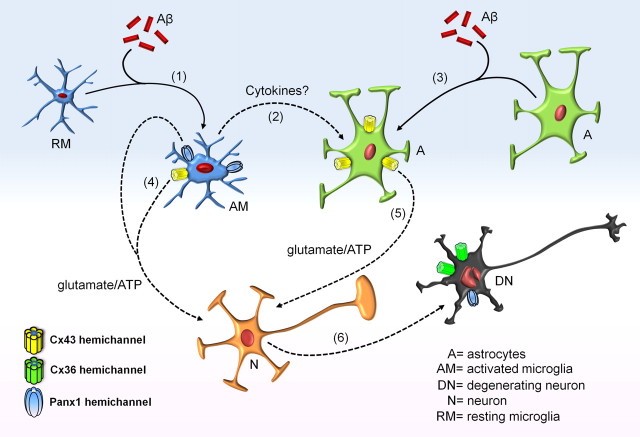
Figure 14.
Model of Aβ-induced cascade resulting in glial and neuronal hemichannel activation leading to neuronal death. Microglia exposed to Aβ peptide become first activated (1), leading to more opening of Cx43 and Panx1 hemichannels. Under these conditions, they release proinflammatory cytokines (2) that contribute to the Aβ-induced Cx43 hemichannel opening in astrocytes (3). Activated microglia might release glutamate and ATP through hemichannels (4), whereas astrocytes could release the same molecules through Cx43 hemichannels (5). This gliotransmission activates neuronal purinergic and NMDA receptors, resulting in an elevation of the intracellular free Ca2+ concentration that might trigger massive Cx36 and Panx1 hemichannel opening increase neuronal vulnerability to ATP and glutamate (6).