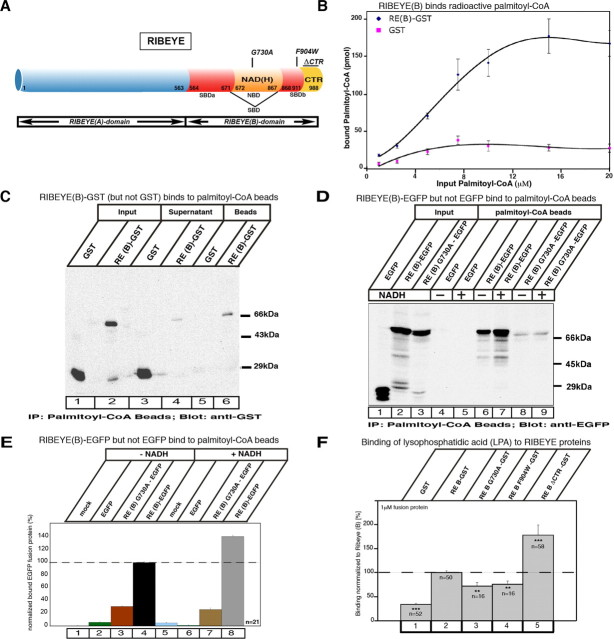
Figure 6.
A, Schematic representation of RIBEYE wild-type protein and RIBEYE point and deletion mutants analyzed in the assays. B–F, RIBEYE binds palmitoyl-CoA (B–E) and LPA (F). B, RIBEYE(B)-GST immobilized to glutathione beads binds radioactive palmitoyl-CoA in a saturable manner. GST reflects background binding. Binding of radioactive palmitoyl-CoA to RIBEYE(B)-GST fusion protein compared to GST is highly significant (p < 0.001; n = 6). C, Binding of soluble RIBEYE(B)-GST fusion protein to palmitoyl-CoA beads. RIBEYE(B)-GST fusion protein binds to palmitoyl-CoA beads, whereas GST fusion protein alone does not. Most of the input RIBEYE(B)GST (lane 2) binds to the palmitoyl-CoA beads (lane 6), whereas only a small portion of RIBEYE(B)-GST remains unbound in the supernatant (lane 4). In contrast, all of the GST input control protein (lane 1) remains unbound in the supernatant (lane 3). D, E, Palmitoyl-CoA binding to RIBEYE is enhanced by NADH. D, Palmitoyl-CoA beads bind EGFP-tagged RIBEYE(B) (lane 6, 7), while EGFP alone (control protein) does not bind (lane 4, 5). RE(B)G730A also binds palmitoyl-CoA (lane 8), but considerably less than RIBEYE wild-type protein (lane 6). Addition of NADH enhances palmitoyl-CoA-binding of RIBEYE(B)-EGFP (lane 7), but not of RIBEYE(B)G730A (lane 9) or EGFP alone (lanes 5). E, Quantification of binding of the indicated RIBEYE proteins and EGFP control protein to palmitoyl-CoA without the addition of NADH (columns 1–4) and with the addition of NADH (columns 5–8). F, Different RIBEYE-proteins were tested for their binding of LPA in the filter tests described in Materials and Methods. Error bars indicate SEM. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.