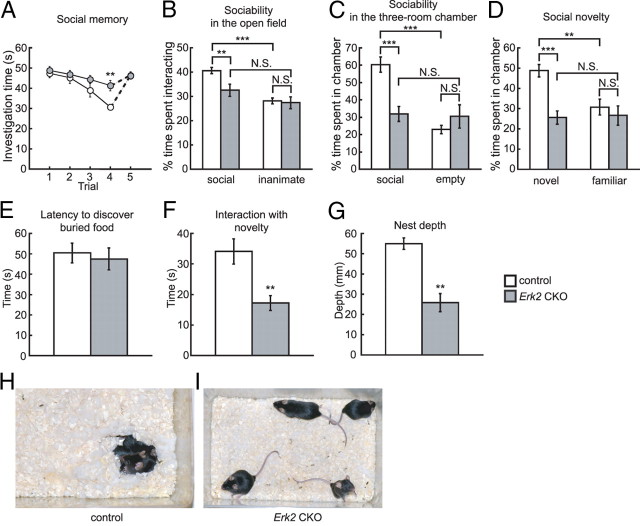
Figure 7.
Erk2 CKO mice are impaired in social behaviors. A–D, Abnormal behaviors in social interaction tests. A, Olfactory investigations in Erk2 CKO mice are used for the social recognition test. Social memory by male mice is measured as the difference in investigation time (control, n = 12; Erk2 CKO, n = 12). The data depict the amount of time spent investigating the same female during each of four successive 1 min trials. A fifth trial depicts the response to a new female. B, When exposed to caged social and inanimate targets in the open field, Erk2 CKO mice show a decreased duration of interaction with the social target, and a similar duration of interaction with the inanimate object (control, n = 29; Erk2 CKO, n = 23). Percentage time is depicted in B–D. C, In the sociability test in a three-room chamber, Erk2 CKO mice spend less time than controls with the social target (control, n = 11; Erk2 CKO, n = 11). D, In the social novelty test, controls show a preference for social novelty, while Erk2 CKO mice show no preference between the novel and familiar targets. Erk2 CKO mice spend significantly less time than controls interacting with the novel target. The same set of mice is used as in C. E, Erk2 CKO mice are not significantly different from controls in the latency to find a buried treat following overnight food deprivation. The same set of mice is used as in B. F, Erk2 CKO mice show a significant decrease in interaction with a novel object in their home cages. The same set of mice is used as in B. G, Erk2 CKO mice show significant deficits in nest formation (control, 6 cages, n = 4 mice per cage; Erk2 CKO, 6 cages, n = 4 mice per cage). H, I, Representative photographs of control (H) and Erk2 CKO (I) cages, 45 min after the introduction of cotton nesting materials into each cage. Note the fluffy nest built in the control cage and the huddling of mice in this nest, in contrast to the poorly formed nests in the Erk2 CKO cage. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. N.S., Not significant.