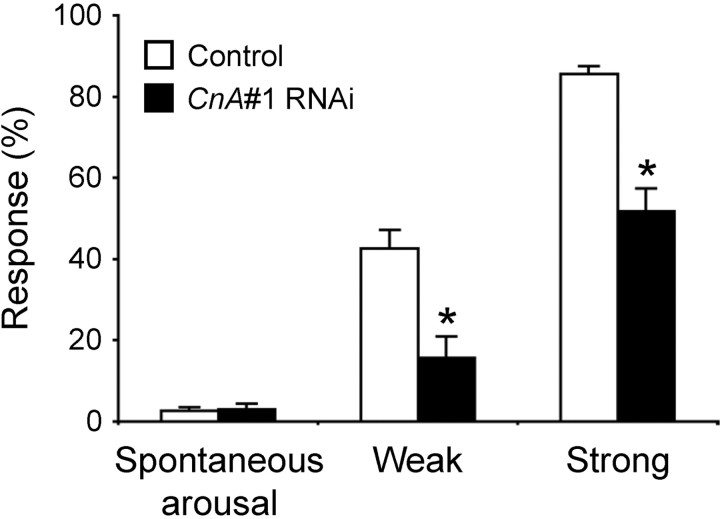
Figure 5.
Hyporesponsiveness to mechanical stimuli of sleeping CnA#1 RNAi flies. Mechanical stimuli were applied to the male flies and response rate (the ratio of the number of aroused flies to the number of the sleeping flies expressed as a percentage) was calculated. Compared with control flies (elav-Gal4;UAS-Dicer-2 × w1118, open bars), the CnA#1 RNAi flies (elav-Gal4;UAS-Dicer-2 × CnA#1, solid bars) showed a smaller response rate to both weak and strong stimuli (n = 19 or 20 for strongly stimulated CnA#1 RNAi flies and other stimulated groups, respectively). In contrast, there was no significant difference in the occurrence of spontaneous arousals (arousals without mechanical stimulations; see Materials and Methods for details) between control and CnA#1 RNAi flies (n = 40 for both genotypes) as calculated from behavioral data. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between control and CnA#1 RNAi flies (Student's t test; p < 0.05). Data are presented as mean ± SEM.