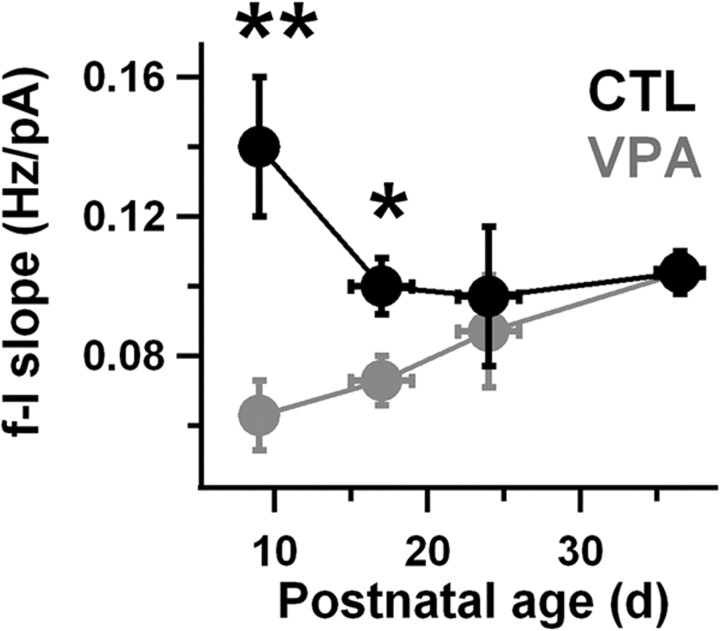
Figure 2.
VPA intrinsic excitability is restored to control levels after the third week of life. The initial slope of the firing rate-current (f–I) curve was measured for each neuron between rheobase and twice rheobase. A mean slope for each animal was calculated by pooling all measurements for neurons from that animal. These means were then divided based on VPA exposure condition and age group (as indicated by the horizontal error bars). Control (CTL) data are in black and VPA data are in gray. The numbers of control and VPA animals in each age range were, respectively: 10 and 10 (P8–P10), 16 and 14 (P15–P19), 5 and 6 (P22–P26), 8 and 8 (P35–P38). On average, four neurons were recorded per animal. For each age group and exposure condition, animals were drawn from 3 to 10 separate litters. Vertical error bars are SEM. VPA exposure was a significant main effect (p < 0.01, ANOVA). Bonferroni tests indicated a significant difference between VPA and control slopes for the two youngest age groups (**p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05).