Figure 3.
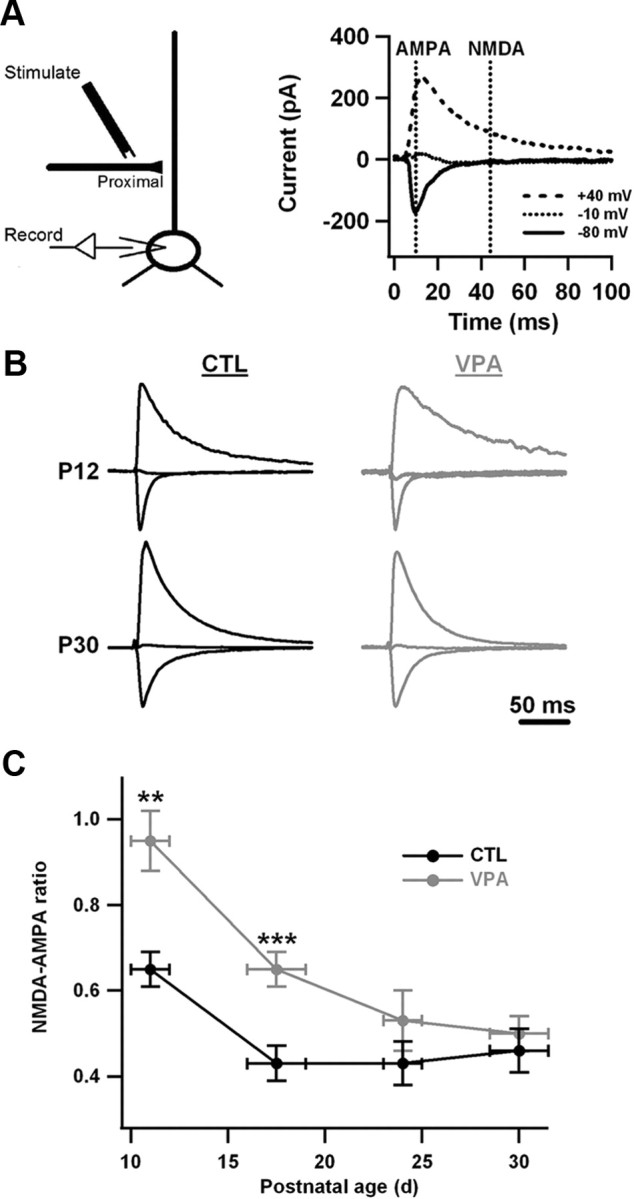
The NMDA-AMPA ratio is elevated in VPA neurons during the early postnatal period but not the late postnatal period. A, The ratio was estimated by stimulating proximal excitatory fibers while holding the postsynaptic neuron in voltage clamp at various potentials Vhold. At the most positive holding potential, the early response was mainly an AMPA current and the late response was mainly an NMDA current. The ratio of these two numbers is what was measured. B, Examples of evoked currents in control and VPA neurons at two ages. The holding potentials were varied as in A. Currents for each neuron have been normalized to the negative-going peak recorded at Vhold = −80 mV. Stimulus artifacts have been zeroed out. C, Average NMDA-AMPA ratio as a function of postnatal age. Horizontal error bars indicate the age ranges into which data were grouped. Vertical error bars are SEM. For control data, the numbers of animals were 7, 8, 3, and 6 for the four age groups shown. For VPA data, the numbers of animals were 6, 8, 3, and 6 for the four age groups shown. On average, four neurons were recorded per animal. For each age group and condition, animals were drawn from 2 to 5 litters. Differences between control and VPA measurements at P10–P12 and P16–P19 were significant (***p < 0.001 and **p < 0.01, Bonferroni test), but those at P23–P25 and P29–P32 were not.
