Figure 9.
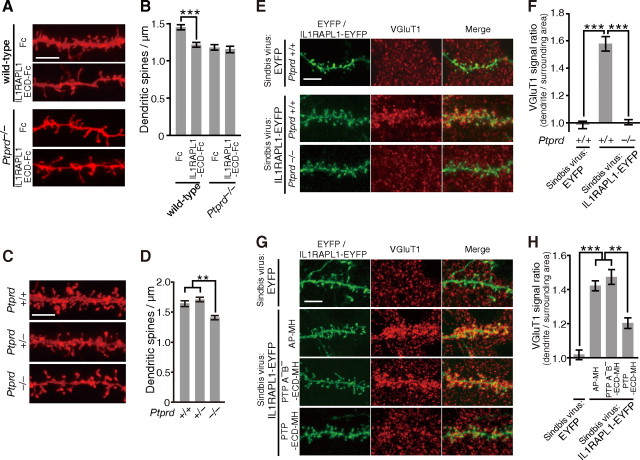
Interaction of IL1RAPL1 and PTPδ mediates synapse formation in vivo. A, PTPδ-dependent decrease in the spine density of basal dendrites of cortical layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons by injection of IL1RAPL1-ECD-Fc. B, Spine densities of basal dendrites of cortical layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons of wild-type and Ptprd−/− mice injected with Fc and IL1RAPL1-ECD-Fc (n = 25–37 neurons from two or three mice). C, Decrease in spine density of basal dendrites of cortical layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons in Ptprd−/− mice. D, Spine densities of basal dendrites of cortical layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons of Ptprd+/+, Ptprd+/−, and Ptprd−/− mice (n = 37–48 neurons from three animals each). E, Immunostaining signals for VGluT1 along the basal dendrites of cortical layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons expressing IL1RAPL1-EYFP in Ptprd+/+ and Ptprd−/− mice. F, Relative densities of immunostaining signals for VGluT1 along the basal dendrites of cortical layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons expressing IL1RAPL1-EYFP in Ptprd+/+ and Ptprd−/− mice (n = 15 neurons from one animal each). Immunostaining signals along the dendrites of the pyramidal neurons expressing EYFP in Ptprd+/+ mouse serve as control (n = 15 neurons from one animal). G, Immunostaining signals for VGluT1 along the basal dendrites of cortical layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons expressing IL1RAPL1-EYFP in the presence of AP-MH, PTPδA−B−-ECD-MH, or PTPδ-ECD-MH. Immunostaining of the pyramidal neurons expressing EYFP serve as control. H, Relative densities of immunostaining signals for VGluT1 along the basal dendrites of cortical layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons expressing IL1RAPL1-EYFP in the presence of AP-MH, PTPδA−B−-ECD-MH or PTPδ-ECD-MH (n = 24–26 neurons from two mice each). Immunostaining signals along the dendrites of the pyramidal neurons expressing EYFP serve as control (n = 13 neurons from one animal). All values represent mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, Student's t test in B and Tukey's test in D, F, and H. Scale bars, 5 μm.