Figure 1.
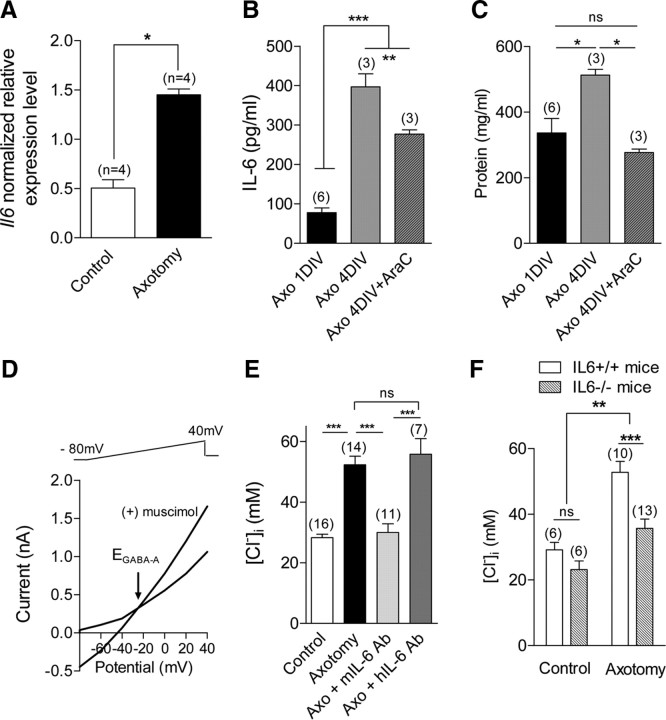
Endogenously produced IL-6 regulates intracellular chloride concentration in sensory neurons. A, RT-qPCR shows a significant increase in mRNA expression of Il6 gene in L4–L5 DRG 3 d after sciatic nerve section. (n, number of experiments with duplicate measure of each gene; *p < 0.05, Mann–Whitney t test). B, Quantitative ELISA measurements of IL-6 production in primary cultures of axotomized neurons from L4–L5 DRGs were performed at days 1 and 4 in vitro. The AraC-sensitive IL-6 production accounted for approximately 30% of total secretion at 4 DIV (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA). C, Corresponding protein content measurements show a significant protein content increase at 4 DIV which was prevented in the presence of 1 μm AraC. (*p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA). D, Gramicidin-perforated patch recordings were used to determine [Cl−]i in sensory neurons. Ramp protocols from −80 mV to +40 mV were applied every 5 s in a Ca-free, Na-free, K-free, 147 mm tetraethylammonium-Cl extracellular solution. Activation of chloride current GABAA with puff application of 50 μm muscimol allowed for determination of reversal potential, EGABAA, of the chloride current and to calculate intracellular chloride concentration (see Materials and Methods). EGABAA was −25 mV in an axotomized sensory neuron, and calculated [Cl−]i was 54 mm. E, Following axotomy, sensory neurons increase their [Cl−]i from 28.3 ± 1.1 mm to 52.3 ± 2.8 mm (***p < 0.001, t test). Incubation of axotomized neurons with 10 μg/ml anti-mouse IL-6 antibody, mIL-6 Ab, significantly decreased [Cl−]i to 30.0 ± 2.8 mm. Incubation with 10 μg/ml hIL-6 Ab, which does not cross-react with the murine IL-6, had no effect on the [Cl−]i of axotomized neurons that amounted to 55.8 ± 5.2 mm (***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA between axotomized conditions). F, EGABAA recordings from IL-6+/+ and IL-6−/− sensory neurons show no significant difference in [Cl−]i under control conditions, which averaged 29 ± 2 mm and 23 ± 2 mm, respectively. The main effect of IL-6 deletion was associated with axotomy. [Cl−]i was significantly higher in axotomized IL-6+/+ sensory neurons (54.5 ± 3.2 mm) than in IL-6−/− axotomized sensory neurons (35 ± 3 mm) (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; two-way ANOVA). Number of experiments is in brackets.