Figure 2.
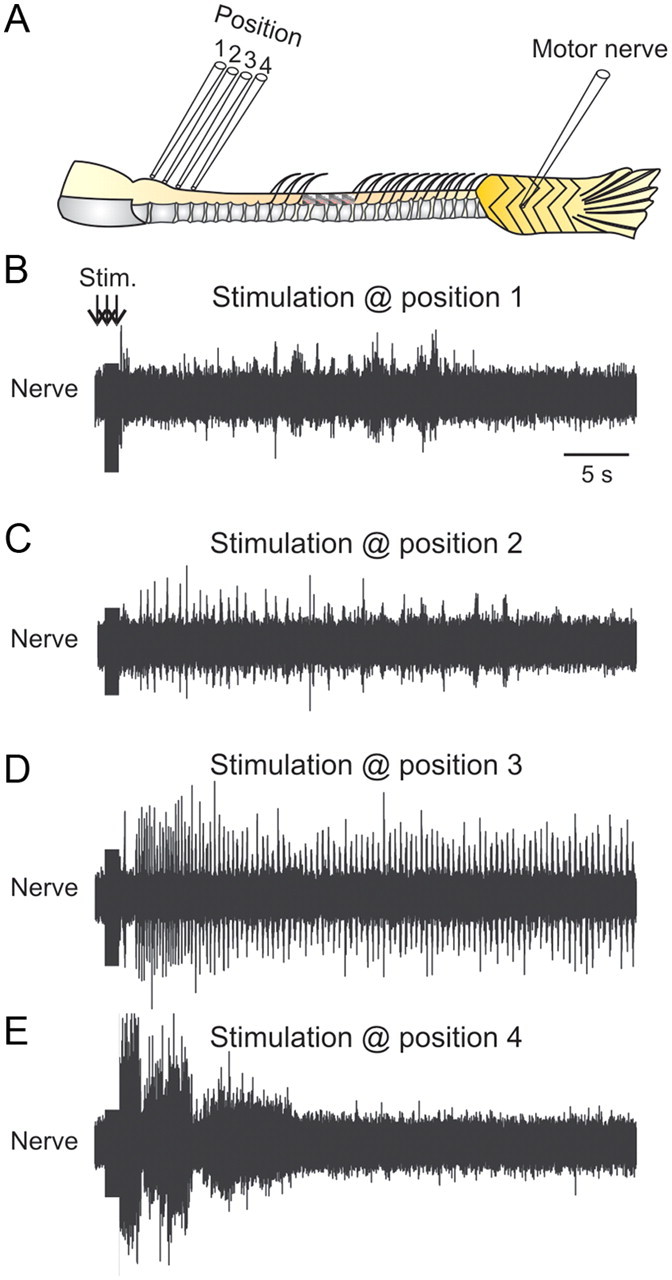
Localization of the optimal position to elicit swimming activity. A, Experimental setup showing the different positions tested to induce swimming activity. B, Stimulation of the rostral brainstem induces only tonic activity. C, Stimulation of the caudal brainstem produces a few bursts recorded in the peripheral motor nerve. D, Stimulation at the junction between the brainstem and spinal cord always induces long-lasting swimming activity. E, Moving the stimulation electrode to a more caudal position only induces tonic activity that does not develop into a swimming pattern.
