Figure 5.
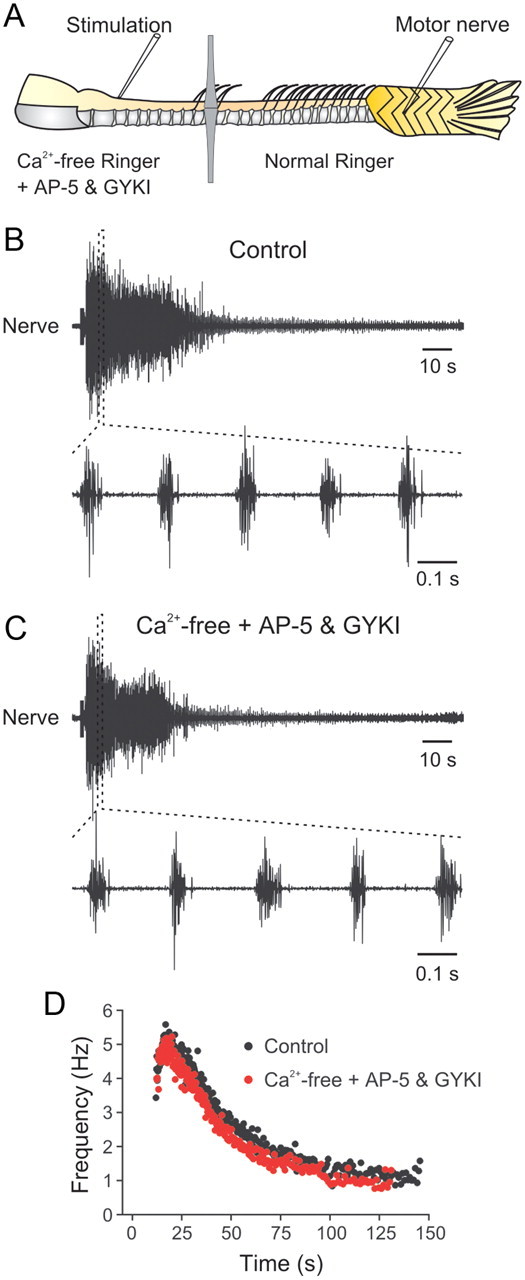
Swimming activity does not depend on synaptic activity between neurons at the site of stimulation. A, Experimental setup with the recording chamber subdivided into two pools that are perfused with physiological solutions of different compositions. B, In normal physiological solution in both pools, swimming activity is elicited by stimulation of the optimal position at the junction between the brainstem and spinal cord. C, Swimming activity can still be elicited when the rostral pool containing the brainstem and the rostral spinal cord is perfused with Ca2+-free solution containing AP-5 and GYKI 52466 to block chemical synaptic transmission and ionotropic glutamate receptors. D, Graph showing the instantaneous frequency during a swimming episode in control and in Ca2+-free solution with ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists.
