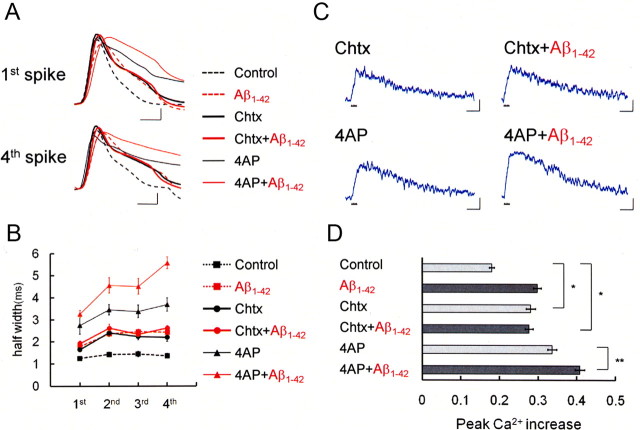
Figure 3.
Intracellular Aβ1-42 enlarges spike width by suppressing BK channels, thereby increasing spike-induced Ca2+ entry. A, First and fourth action potentials during spike trains after application of the BK channel blocker Chtx (50 nm) or the A-type K+ channel blocker 4-AP (5 mm) in a control cell (Chtx: thick black trace, n = 7; 4-AP: thin black trace, n = 5) and an Aβ1-42-injected cell (Chtx+Aβ1-42: thick red trace, n = 4; 4-AP+Aβ1-42: thin red trace, n = 4). The action potentials in the control cell (black dashed trace) and Aβ1-42-injected cell (red dashed trace) shown in Figure 1 are superimposed. Calibration: 1 ms, 20mV. B, Averaged spike half-width during four-spike trains with no blocker (black square, Control; red square, Aβ1-42), with charybdotoxin (black circle, Control; red circle, Aβ1-42) and with 4-AP (black triangle, Control; red triangle, Aβ1-42). C, Spike-induced Ca2+ increase under application of charybdotoxin or 4-AP in control or Aβ1-42-injected neurons. Calibration: 500 ms, −0.1ΔF380/F360. D, Summary diagram demonstrating average Ca2+ increases in the control, charybdotoxin, and 4-AP groups, each with and without Aβ1-42. In B and D, charybdotoxin, but not 4-AP, mimicked and occluded the effect of Aβ1-42. *p < 0.0001; **p < 0.01.