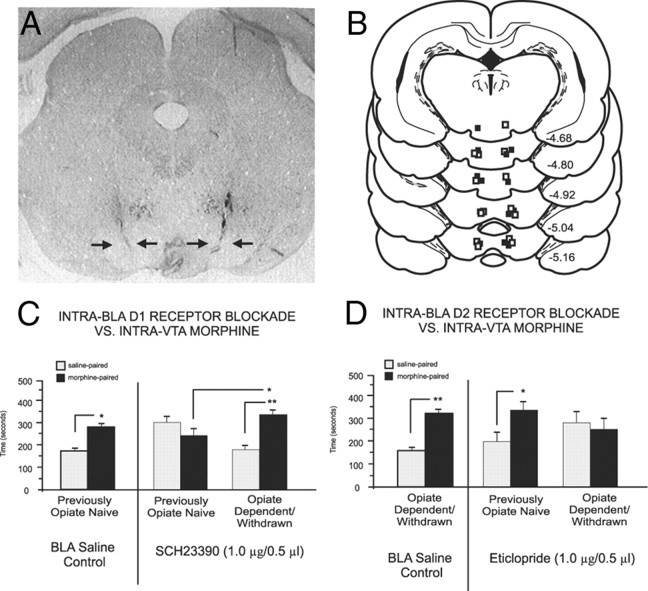
Figure 4.
Intra-VTA microinfusion placements and effects of intra-BLA D1-like or D2-like receptor blockade on intra-VTA morphine reward processing. A, Microphotograph showing representative bilateral intra-VTA injector tip locations. B, Schematic representation of representative intra-VTA bilateral injector locations. ■ = Previously opiate-naive rats receiving intra-BLA SCH 23390 (1.0 μg/0.5 μl); □ = opiate-dependent/withdrawn rats receiving intra-BLA eticlopride (1 μg/0.5 μl). C, Intra-VTA morphine produces robust CPP for intra-VTA morphine environments (500 ng/0.5 μl) in previously opiate-naive control rats receiving intra-BLA saline. However, intra-BLA SCH 23390 (1.0 μg/0.5 μl) blocks the acquisition of CPP to environments paired with intra-VTA morphine (500 ng/0.5 μl) only in previously opiate-naive rats. D, Intra-VTA morphine produces robust CPP for intra-VTA morphine (500 ng/0.5 μl) environments in opiate-dependent/withdrawn control rats receiving intra-BLA saline. However, intra-BLA eticlopride (1.0 μg/0.5 μl) blocks the acquisition of CPP to environments paired with intra-VTA morphine (500 ng/0.5 μl) only in opiate-dependent/withdrawn rats but not in previously opiate-naive rats.