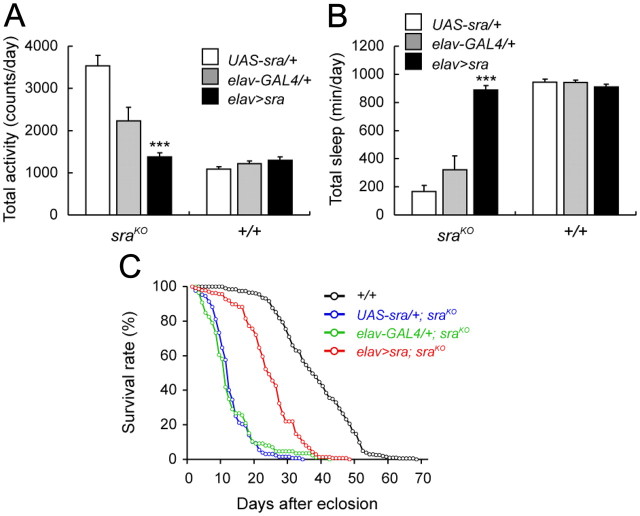
Figure 3.
Expression of sra in neurons rescues activity, sleep and lifespan phenotypes of sraKO mutants. A, Daily activity of UAS-sra/+; sraKO and elav-GAL4/+; sraKO flies is significantly higher than wild type, while activity in elav>sra; sraKO flies is reduced back to wild-type levels. Neuronal expression of sra in a wild-type background has no effect on activity. B, Neuronal expression of sra rescues sraKO sleep defects (elav>sra; sraKO), while it has no effects in a wild-type background. Driver alone and UAS-sra alone controls do not rescue sraKO sleep defects. In A and B, *** indicates significant differences between elav>sra and both UAS-sra alone and elav-GAL4 alone controls in the sraKO background (p < 0.001). No significant differences were detected in the +/+ background. C, Survival curves for male wild-type (+/+), elav>sra; sraKO, elav-GAL4/+; sraKO, and UAS-sra/+; sraKO flies. Neuronal expression of sra partially rescues the reduced lifespan of sraKO mutants. Wild-type males have an average lifespan of 37.82 ± 0.76 d, while elav>sra; sraKO, elav-GAL4/+; sraKO, and UAS-sra/+; sraKO flies have average lifespans of 24.30 ± 0.70, 12.60 ± 0.83, and 12.65 ± 0.48 d, respectively.