Figure 1.
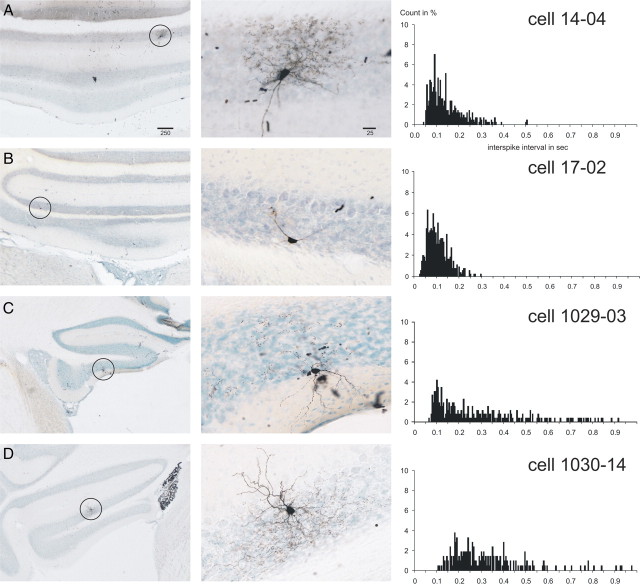
Juxtacellularly labeled rat Golgi cells with the ISI histograms of their respective spontaneous activity. A–D show four representative Golgi cells from the vestibulocerebellum. The left-hand column shows microphotographs of an overview of the location of the labeled cell, which is indicated with a circle. The middle column shows a detail of the labeled cell. The right-hand column shows the ISI histograms based on 60 s of spontaneous firing (bin width, 5 ms; count in percentage of total counts). Note the dense axonal terminal arborizations of the cells shown in A and D. The cell in C also had similar arborizations best seen in the adjacent section. The cell in B represents large granular layer interneurons that did not show dense terminal arborizations but that also did not fit descriptions of other granular interneuronal types, such as the Lugaro or candelabrum neuron (Lainé and Axelrad, 1994, 1996) or UB cells. The ISI histogram of the cell in B was similar to that of the morphologically typical Golgi cells. Scale bars in A are in micrometers and also apply to B–D. The cell shown in A was also shown in the study by Simpson et al. (2005).