Figure 6.
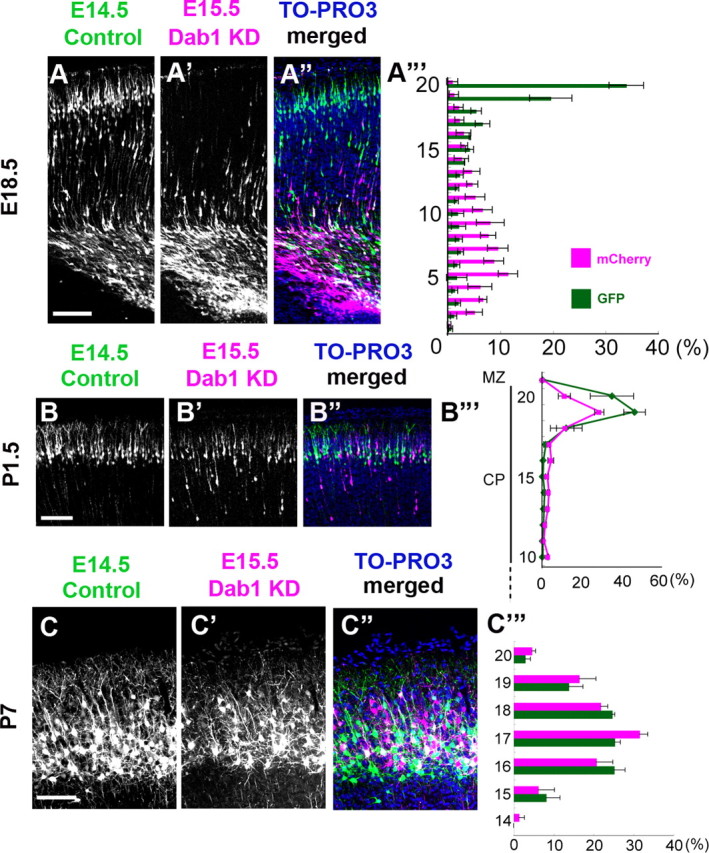
Dab1 is required for the eventual inside-out alignment of the mature cortex. A–A‴, Control-Dab1–KD case at E18.5. The distributions of the GFP-labeled earlier-born control neurons and the mCherry-labeled later-born Dab1–KD neurons were almost the same as those in the control–control case (Fig. 5A-A‴). A‴, Bin analysis. The distance between the outer margin of the CP and the inner margin of the IMZ was divided into 20 bins. Scale bar, 100 μm. n = 3 brains. B–B‴, Control–Dab1–KD case at P1.5. The mCherry-labeled later-born Dab1–KD neurons were seen at almost the same position as the GFP-labeled earlier-born control neurons. B‴, Bin analysis. The distance between the outer margin of the CP and the inner margin of the IMZ was divided into 20 bins. The later-born Dab1–KD neurons were seen in the 19th bin, which was almost similar to the case of the earlier-born control neurons. Scale bar, 100 μm. n = 4 brains. C–C‴, Control–Dab1–KD case at P7. The mCherry-labeled later-born Dab1–KD neurons were located at almost the same position as the GFP-labeled earlier-born control neurons, showing disruption of the inside-out alignment pattern. C‴, Bin analysis. The thickness of the CP was divided into 20 bins. The distribution of the later-born Dab1–KD neurons was similar to that of the earlier-born control neurons. The mean ± SEM distances from the top of the CP were 132.9 ± 16.1 μm for the GFP-labeled neurons and 124.4 ± 10.3 μm for the mCherry-labeled neurons, respectively (p = 0.8273, Mann–Whitney's test, n = 3 brains, >800 neurons were counted.). Scale bar, 100 μm.
