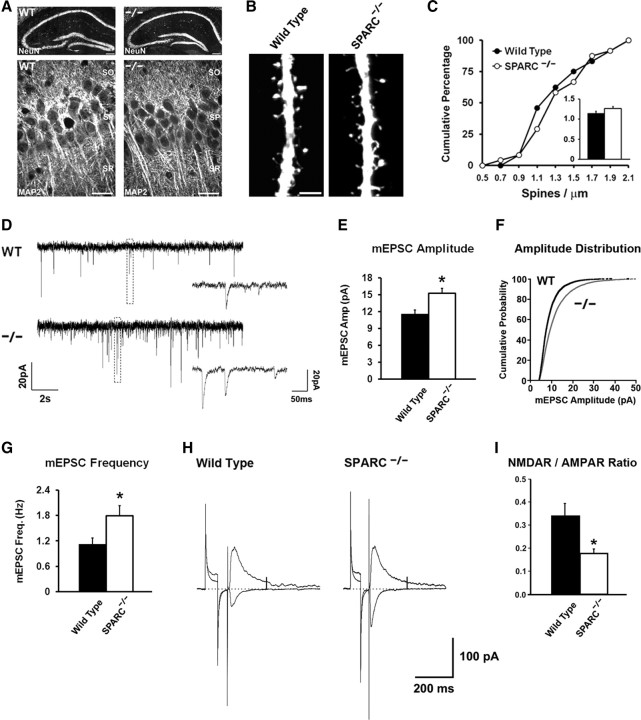
Figure 2.
SPARC KO mice show enhanced synaptic strength and alterations in NMDAR/AMPAR ratios. A, NeuN and MAP2 immunolabeling (P27 hippocampus) indicating that hippocampal architecture and dendritic structure is similar in WT and KO mice. B, Representative images of CA1 apical dendrites expressing membrane-targeted mCherry in WT and KO organotypic slices. C, Quantification of spine density between WT and SPARC KO neurons (Mann–Whitney U, p = 0.5362) D, Sample traces of mEPSC recordings from hippocampal pyramidal neurons of WT (top) and SPARC KO (bottom) organotypic hippocampal slices. E, Graph of average mEPSC amplitudes showing significant increases in amplitudes in SPARC KO neurons (2-tailed t test, *p = 0.0073). F, Cumulative distribution of mEPSC amplitudes from cells shown in the histogram (K–S test, p < 0.001). G, Graph of average mEPSC frequencies showing a significant increase in SPARC KO neurons (2-tailed t test, *p = 0.0375). H, Representative current traces of AMPAR-mediated inward currents (−60 mV) and mixed NMDAR+AMPAR-mediated outward currents (+40 mV) recorded from hippocampal neurons in acute WT and SPARC KO slices. I, SPARC KO mice show a significant reduction in the ratio of NMDAR/AMPAR currents (2-tailed t test, *p = 0.0154). Scale bars: A, top panels, 100 μm; bottom panels, 20 μm; B, 3 μm.