Figure 5.
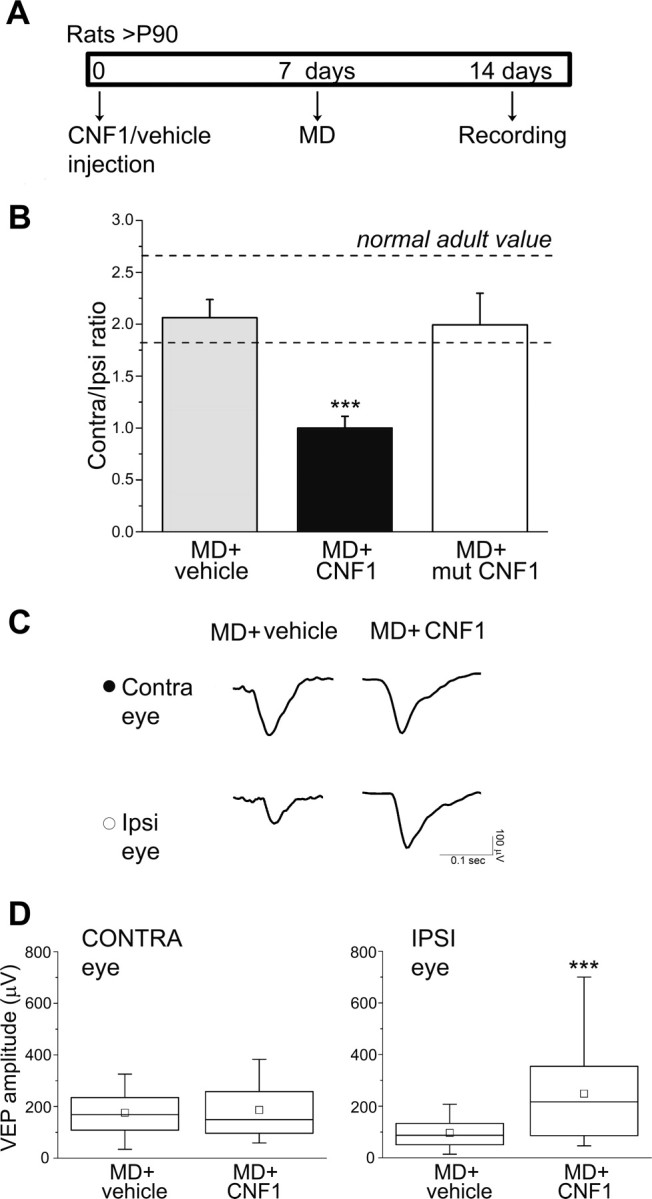
Activation of Rho GTPases reinstates OD plasticity in the adult cortex via potentiation of inputs from the ipsilateral, open eye. A, Experimental protocol. B, C/I VEP ratios in MD animals treated with vehicle (MD + vehicle; n = 11), with CNF1 (MD + CNF1; n = 8) and with a mutated form of CNF1 (MD + mut CNF1; n = 5). In MD + vehicle rats, the C/I ratio is unchanged (post-ANOVA Holm–Sidak test, p = 0.52) compared with the normal adult range (indicated by the dashed lines), whereas in MD + CNF1 animals, there is a dramatic decrease of the C/I ratio (p < 0.001). Injection of a mutated form of CNF1 (mut CNF1) is completely ineffective in shifting OD (MD + mut CNF1 vs MD + vehicle, p = 0.8; MD + mut CNF1 vs MD + CNF1, p = 0.002). Data are mean ± SEM. Normal adult range: mean ± SD value. C, Representative examples of VEP responses for both eyes in MD + vehicle (left column) and MD + CNF1 (right column) rats. Visual stimulus: square-wave grating alternating at 1 Hz, spatial frequency of 0.07 cycles/°, contrast at 90%. CONTRA, Contralateral deprived eye; IPSI, ipsilateral open eye. D, Quantitative analysis of absolute VEP amplitudes in MD + vehicle (n = 11) and MD + CNF1 (n = 8) rats. There is no difference in contralateral eye VEP amplitude between the two groups (Mann–Whitney rank-sum test, p = 0.75, left), whereas ipsilateral eye VEPs are significantly enhanced in CNF1-injected rats (Mann–Whitney rank-sum test, p < 0.001, right). ***p < 0.001.
