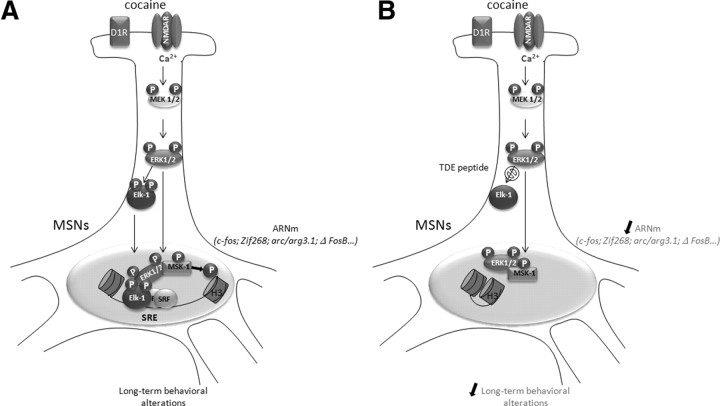
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of molecular events driven by Elk-1 phosphorylation in response to cocaine. A, During cocaine administration, combined activation of D1R and NMDAR drives ERK activation via calcium entry (Pascoli et al., 2011). This leads to the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of Elk-1 along with ERKs. Within the nucleus, Elk-1 binds to the SRE sites of IEGs (including c-fos, zif268, and arc/arg3.1) and recruits ERK1/2 and MSK-1 at the proximity of the nucleosome. In turn, MSK-1 can phosphorylate histone H3 on Ser10 residue, allowing nucleosome repositioning and transcription. These molecular events are critically involved in MSN spine plasticity and long-term behavioral alterations in response to cocaine. B, In the presence of the TDE peptide, Elk-1 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation is impeded. Cocaine-induced ERK and MSK-1 phosphorylation persist, but MSK-1 is not recruited to the nucleosome. SRE-driven gene regulation is inhibited, along with spine plasticity and long-term behavioral responses.