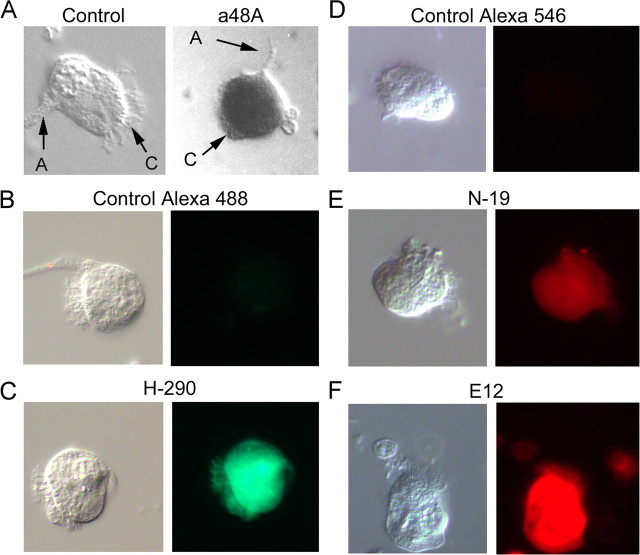
Figure 3.
Single-cell labeling with anti-arrestin antibodies. To refine the localization of arrestin, Pecten retinae were enzymatically dissociated, and isolated cells were plated and fixed, before incubation with antibodies. A, Left, Micrograph of a control ciliary cell only exposed to alkaline phosphatase-conjugated secondary antibodies (A, axon; C, cilia; S, soma). Right, Photoreceptor treated with anti-visual arrestin primary antibody (a48K). B, Control cell exposed to anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (×rb) conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488. C, Ciliary photoreceptor treated with rabbit anti β-arrestin antibody H-290 and ×rb-Alexa Fluor 488 secondary antibodies. D, Control treated with anti-goat (×gt) Alexa Fluor 546. E, Single-cell immunostaining with the anti β-arrestin antibody N-19, and fluorescent secondary antibodies ×gt-Alexa Fluor 546. F, Ciliary photoreceptor treated with goat anti-visual arrestin antibody E-12, secondary ×gt-Alexa Fluor 546. These observations confirm the presence of arrestin immunoreactivity within identified ciliary photoreceptors.