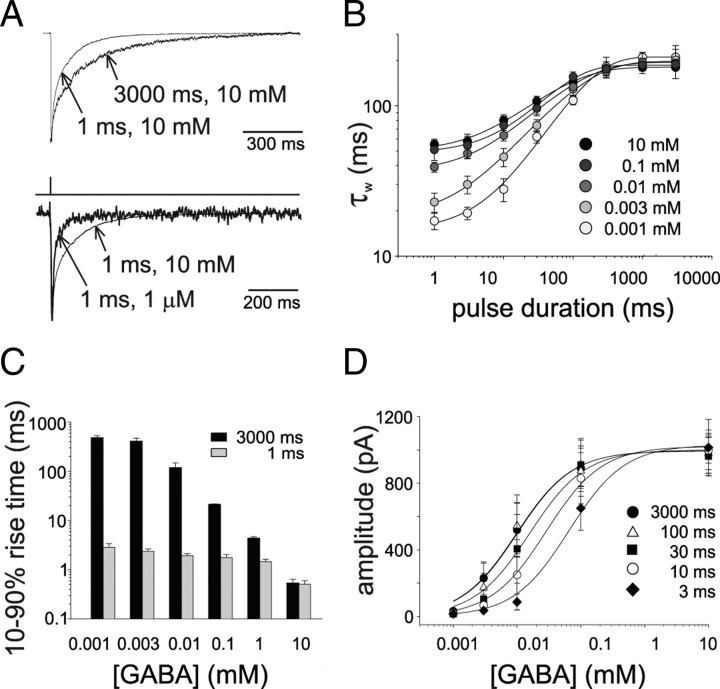
Figure 1.
Dependence of α1β2γ2-mediated current kinetics on GABA concentration and pulse duration. A, Top, Current traces obtained by exposing patches to brief (1 ms) or long (3000 ms) pulses of saturating [GABA]. For reasons of clarity, GABA application protocol is not indicated since the two traces are elicited by different duration pulses. Bottom, Currents evoked by (1 ms) pulses of 10 and 0.001 mm GABA. Note the faster current deactivation at low GABA concentrations. B, Summary of the dependence between GABA pulses duration and weighted current decay time constant obtained at different [GABA]. C, Summary of the dependence of 10–90% rise time of the current elicited by long (black) and short (gray) pulses on GABA concentration and pulse duration. D, Dose dependence of current amplitude at various GABA pulse durations (EC50 = 12.2 ± 1.8 μm at 3000 ms pulses). Each data points results from at least 20 recordings.