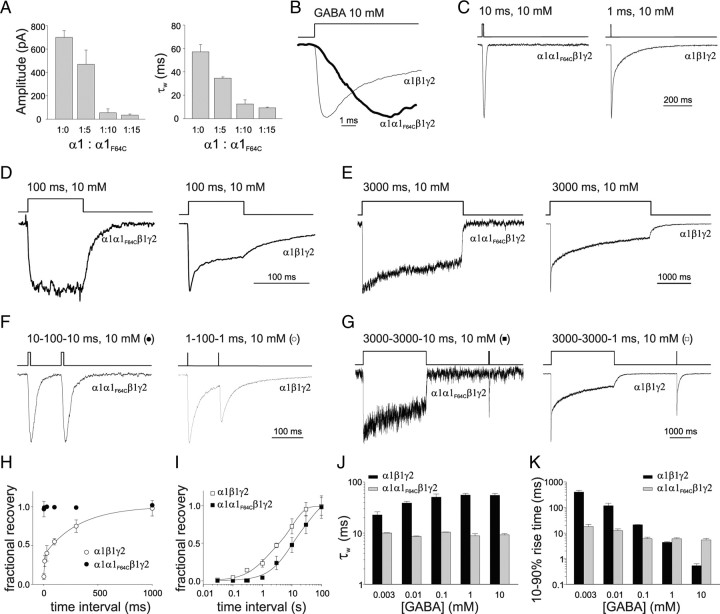
Figure 4.
Characterization of α1α1F64Cβ1γ2 receptor gating properties. A, Summary of the dependence of current amplitude (left) and decay kinetics (right) upon the ratio between α1 and α1F64C overexpression. B, The 10–90% rise time of normalized α1α1F64Cβ1γ2 (thick line) and α1β1γ2 (thin line) currents. C, Comparison of the deactivation kinetics between α1α1F64Cβ1γ2 (left) and α1β1γ2 (right) normalized currents. D, Desensitization induced by 100 ms, 10 mm GABA pulse in α1α1F64Cβ1γ2 (left) and α1β1γ2 (right) receptors. E, Desensitization induced by 3000 ms, 10 mm GABA pulse in α1α1F64Cβ1γ2 (left) and α1β1γ2 (right). F, Currents elicited by two consecutive 10 ms pulses spaced by 100 ms from α1α1F64Cβ1γ2 (left) and α1β1γ2 (right) receptors. G, Typical response of α1α1F64Cβ1γ2 (left) and α1β1γ2 (right) currents to long (3000) ms conditioning pulse followed by a short (10 ms) test pulse. H, Summary of recovery from desensitization of paired pulse experiments shown in F. α1α1F64Cβ1γ2 currents (black circles), at the considered time points, showed immediate recovery, while the α1β1γ2 receptors (open circles) displayed biexponential recovery (τfast = 8 ± 0.2 and τslow = 321 ± 21 ms, Afast = 0.36 ± 0.03). I, Summary of recovery from desensitization of paired pulse experiments shown in G. Both α1α1F64Cβ1γ2 currents (black squares) α1β1γ2 currents (open squares) showed biexponential recovery (τw = 27.3 ± 2.7 and τw 8.4 ± 1.1 s, respectively). J, Summary of the dependence of α1β1γ2- and α1α1F64Cβ1γ2 currents deactivation kinetics on [GABA] (black, 1 ms pulse; gray, 20 ms pulse). K, Summary of the dependence of α1β1γ2- and α1α1F64Cβ1γ2 currents onset kinetics on [GABA] (3000 and 20 ms pulses for black and gray, respectively). Each data point results from at least 20 recordings.