Figure 8.
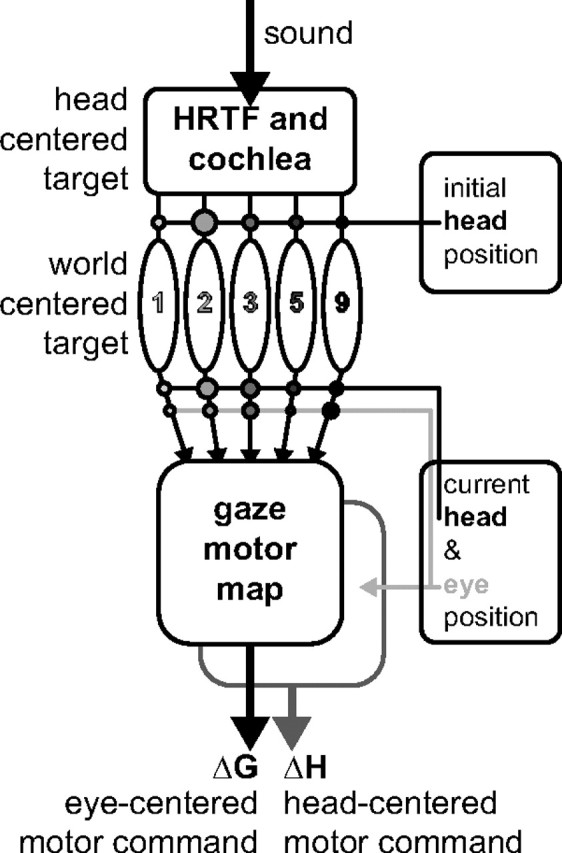
Conceptual scheme of the audio-motor system. Sound is filtered by the pinna-related head-related transfer functions (HRTF) before reaching the cochlea, which encodes a head-centered target location. The ascending auditory pathway is tonotopically organized. Initial head position interacts in a frequency-specific way (connectivity strength indicated by circles) to represent a world-centered target representation in the population of narrow-band channels. To program the eye–head gaze shift, signals about current head and eye position interact with the world-centered target signal at the level of the tonotopic arrays, and at the SC gaze-motor map. The eye-centered gaze command thus depends on eye and head position. The head-motor command only depends on current eye position (light-gray arrow). In this way, the eye-in-space and the head are driven by different neural commands: ΔG and ΔH.
