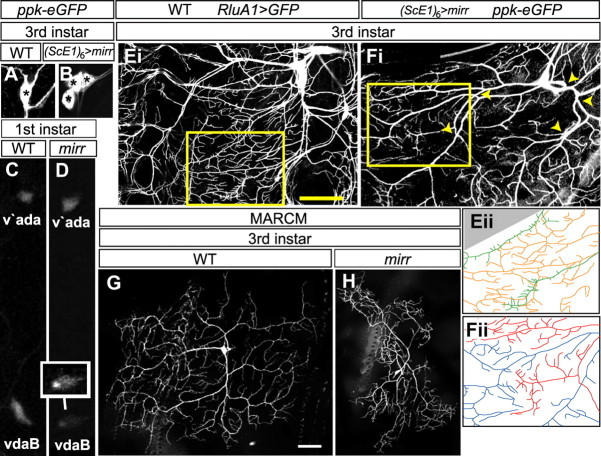
Figure 5.
Mirr is required for vdaB class IV-specific differentiation. A, B, WT (A) and (ScE1)6-Gal4, UAS-mirr, ppk-eGFP (B) third instar larvae stained with an anti-GFP antibody. WT larvae have one ppk-eGFP-positive class IV neuron in the ventral cluster. (ScE1)6-Gal4, UAS-mirr larvae have 2 or 3 ppk-eGFP-positive neurons. Asterisks mark the individual cell bodies. C, D, WT (C) and mirr mutant (D) first instar larvae showing ppk-eGFP expression in ventral (vdaB) and ventral prime (v'ada) class IV neurons. To highlight vdaB, the inset neuron in D has the fluorescence levels in this neuron accentuated via image processing software. Ei, The ventral cluster of a WT third instar larva where all MD neurons and their dendritic arbors are marked via RluA1-Gal4, UAS-mCD8::GFP (Jinushi-Nakao et al., 2007). Eii, A tracing of dendrite branches in the area highlighted with a yellow box in Ei, class IV dendrites are colored orange and class III green. Extensive overlap of the dendritic termini of these different neuron classes occurs. Fi, The ventral cluster of a (ScE1)6-Gal4, UAS-mirr, ppk-eGFP larva. The vdaB and a second transformed neuron both express ppk-eGFP that marks their dendritic arbors. The major trunks of these neighboring dendrite arbors overlap (yellow arrowheads). Fii, A tracing of the area highlighted with a yellow box in Fi, The dendrite arbor is colored red for one neuron and blue for the other. The dendritic termini of these two neurons do not overlap, instead they partition the body wall into small domains. G, H, WT (G) and mirr MARCM vdaB (H) clones in a third instar larva. mirr mutants show a failure to properly arborize over the normal dendritic field area. Scale bars, 35 μm.