Figure 3.
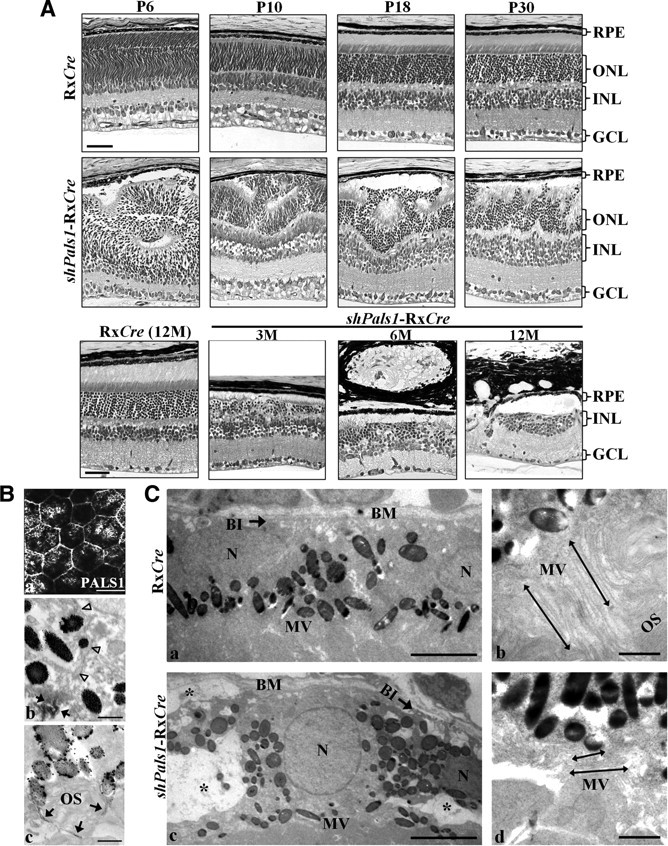
Decreased levels of PALS1 in shPals1-RxCre retinas caused retinal degeneration and abnormal RPE structure. A, Technovit retinal sections of control RxCre mice at postnatal day 6 (P6), P10, P18, and P30 and 12 months of age (12M), and shPals1-RxCre mice at P6, P10, P18, and P30 and 3, 6, and 12 months of age (3M, 6M, 12M). The phenotype in shPals1-RxCre retinas is detectable initially at the peripheral part of the retina at P6, and it spreads to the entire retina following retinal maturation. Even though the retinal layers (ONL, INL, GCL) are separated, retinal folds and half rosettes of the ONL are detected, and photoreceptor nuclei protruded into the subretinal space and ingressed into the OPL from P10 onwards. In aged mutant retinas (3–12M), the ONL and OPL become thinner due to gradual retinal degeneration. The ONL is also severely damaged and abnormal large vacuoles are detected in the RPE layer. Scale bar, 50 μm. B, Representative PALS1 staining images from immuno-EM and IHC analysis are shown from wild-type at P10. a, IHC flat mount of RPE cells stained with anti-PALS1. At immuno-EM level, the RPE monolayer has apical microvilli toward the photoreceptor outer segments and the cells are interconnected by tight junctions (b, c). Arrowheads indicate the basolateral membrane. b, c, Arrows indicate PALS1 at the tight junction (b) and in apical microvilli surrounding a photoreceptor outer segment (c). Scale bars: 20 μm (a), 0.5 μm (b, c). C, EM analysis of RxCre and shPals1-RxCre mice at P10. RPE cells appeared to be disorganized with short microvilli (double-headed arrows in d), reduced/disorganized basal infoldings (arrow in c), and in addition, numerous vacuoles were present within the cells (c, asterisk). N, RPE cell nucleus; OS, photoreceptor outer segments; Mv, microvilli; BM, Bruch's membrane; BI, basal infoldings. Scale bars: 5 μm (a, c), 1 μm (b, d).
