Figure 2.
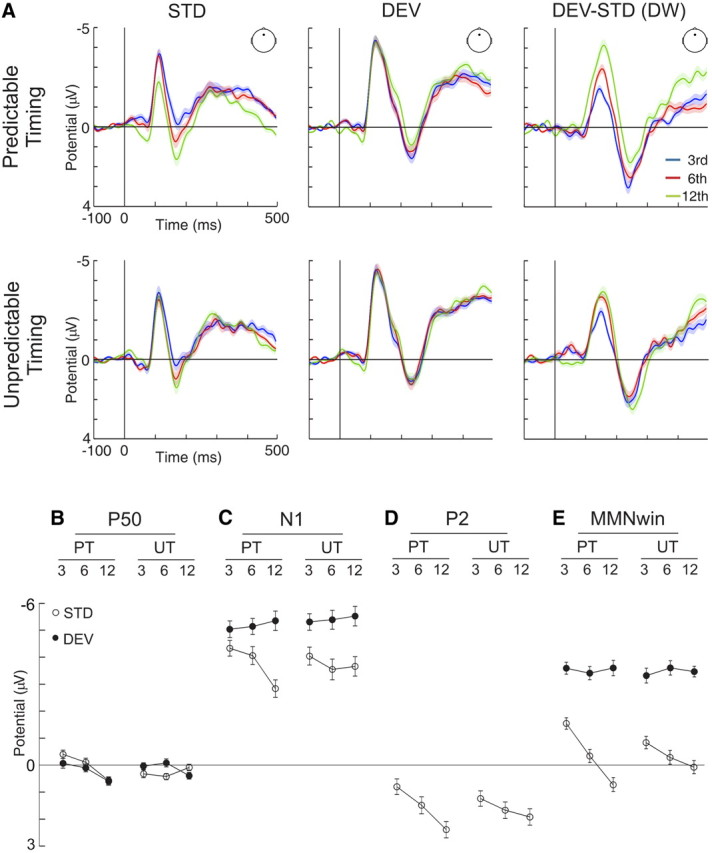
A, Grand-average waveforms for standard (STD), deviant (DEV), and deviant minus standard differences (DEV-STD DW) in predictable (top) and unpredictable (bottom) timing conditions, separately for trains of three (blue trace), six (red trace), and 12 (green trace) tone presentations, as recorded from Fz electrode. Shaded areas indicate SEM. B, P50 amplitudes in predictable (PT) and unpredictable (UT) timing conditions elicited to standard (white circles) and deviant (black circles) stimuli separately for trains of three, six, and 12 tones (amplitudes in microvolts; error bars denote SEM). P50 amplitude increased with repetition only in the predictable timing condition regardless of stimulus type. C, Same as B, but for N1 amplitudes, which were overall larger for deviant than standard stimuli but decreased with further repetition only for standard stimuli in the predictable timing condition. D, Same as B, but for P2 amplitudes elicited to the standard stimulus. P2 amplitudes increased with tone repetition regardless of timing predictability. E, Same as B, but for amplitudes retrieved in a time window around the MMN. Deviant stimuli elicited more negative amplitudes in the MMN time window (MMNwin) than standard stimuli, but only the latter were affected by repetition, an effect manifested as an increase of positivity, larger in the predictable than the unpredictable timing condition.
