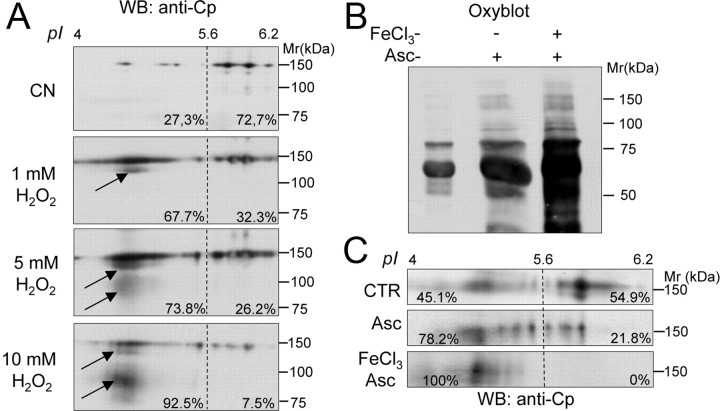
Figure 3.
In vitro oxidative stress induces Cp to convert to acidic isoforms and total CSF protein carbonylation to increase. A, WB analysis of Cp profile in the CSF from a representative CN subject resolved by 2DE under resting conditions or after treatment with increasing amounts of H2O2 (1, 5, 10 mm); percentages indicate the amount of total Cp signal present in regions A and B (Fig. 1); the arrows indicate low-molecular-weight products generated by protein oxidation. B, Detection of protein carbonylation by OxyBlot assay on total CSF proteins resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained for carbonyl groups, under resting conditions or after oxidation obtained by treatment with Asc with or without ferrous chloride (FeCl3). C, WB analysis of 2DE Cp profile in the CSF under resting conditions or after oxidation treatments as in B; percentages indicate total Cp signal present in regions A and B (Fig. 1).