Figure 1.
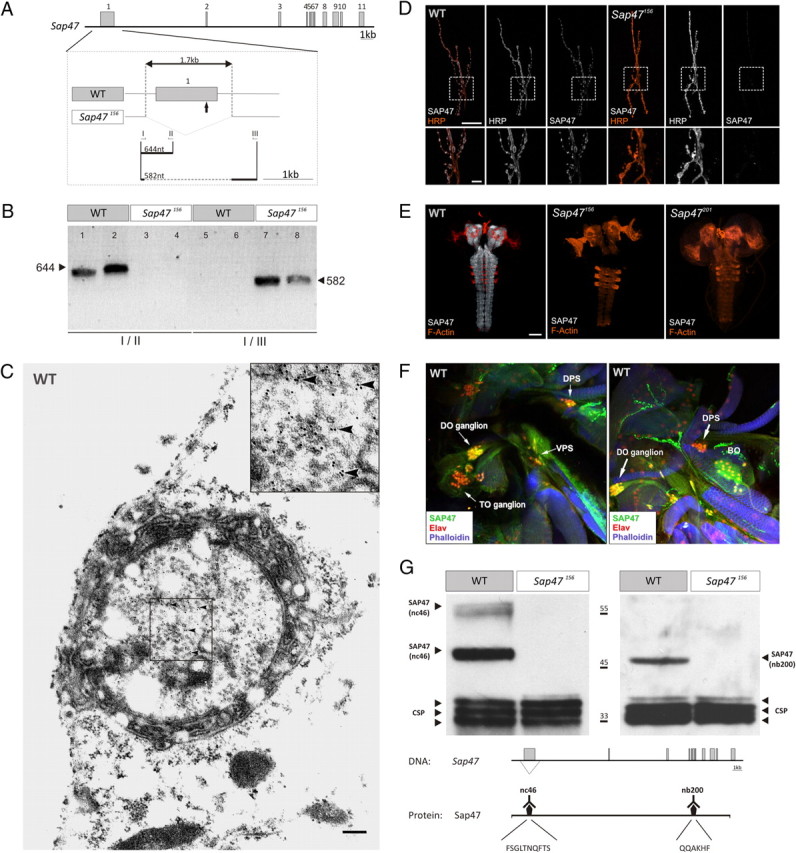
Characterizing the Sap47 gene and the Sap47156 mutant. A, Gene structure. Shown is the exon–intron structure of the Sap47 gene in wild type (WT: exons gray). The deletion in Sap47156 is shown in higher magnification. The arrow below the first exon indicates the translation start. Other arrows and roman numerals indicate binding sites of primers used for PCR in B. B, PCR. PCR with primer pair I/II generates a 644 bp fragment only in WT, because there is no binding site for primer II in the Sap47156 mutant; primer pair I/III generates a 582 bp fragment only in the Sap47156 mutant, because an elongation time was chosen that is too short for amplification of the long WT fragment. Two samples were run for each condition. C, Electron microscopy. Shown is a synaptic bouton with synaptic vesicles and immunolocalization of SAP47 in a WT larva using electron microscopy at the larval neuromuscular junction. Bound primary mouse anti-SAP47 antibodies were detected with gold-conjugated secondary anti-mouse antibodies. Gold particles (arrowheads) are localized close to synaptic vesicles. The inset represents the boxed area in higher magnification. Scale bar, 200 nm. D, Neuromuscular junction. At the neuromuscular junction (muscle pair 6/7), the Sap47156 strain does not show any anti-SAP47 immunoreactivity, whereas in WT, synaptic boutons are stained (white). Preparations are double labeled with a Texas Red-coupled anti-HRP antibody to label cell membranes (orange), and the nc46 antibody to label SAP47, and are viewed under a confocal microscope. Scale bar, 20 μm. The lower panels represent an enlarged view of the boxed area. Scale bar, 5 μm. E, Whole-mount larval brains. In both mutant strains (Sap47156 and Sap47201), no anti-SAP47 immunoreactivity is detectable in whole-mount preparations of the larval brain, whereas the neuropil regions in WT are strongly stained [antibody: nc46 (white)]. For orientation, F-actin is visualized with phalloidin (orange). Scale bar, 50 μm. F, Cephalic sensory systems. SAP47 immunoreactivity is detectable in single confocal slices of the cephalic sensory systems of third-instar WT larvae. DO, TO, the dorsal, posterior, and ventral pharyngeal sense organs [DPS, PPS (not shown), and VPS], and the Bolwig organ are at least partially stained [antibody: nc46 (green)]. For orientation, F-actin is visualized with phalloidin (blue) and an anti-Elav antibody is used to stain neuronal nuclei (red). Note that in the DO ganglion SAP47 is found in cell nuclei. G, Western blot. There is no SAP47 signal detectable on Western blot in the Sap47156 mutant, whereas WT shows the expected (Reichmuth et al., 1995; Funk et al., 2004) strong band at 47 kDa with both monoclonal antibodies used [left: nc46, with its epitope FSGLTNQFTS, which is within the Sap47156 deletion; right: nb200, with its epitope QQAKHF, which is downstream, C-terminal of the Sap47156 deletion (Hofbauer et al., 2009)]. As loading control, a monoclonal antibody against the synaptic protein CSP is used (antibody: ab49).
