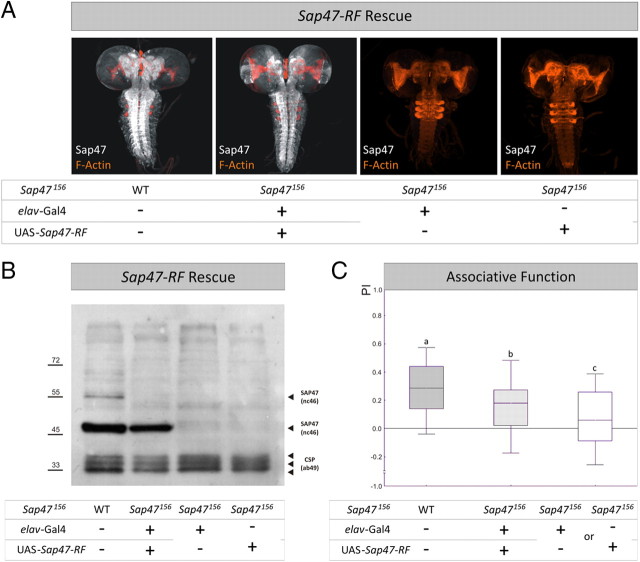
Figure 6.
SAP47 rescue with 47 kDa isoform. A, Whole mounts. In contrast to WT and rescue larvae, the elav-Gal4; Sap47156 driver-control and the UAS-Sap47-RF; Sap47156 effector-control strains show no SAP47 expression. Phalloidin is used to visualize F-actin (orange). B, Western blot. In contrast to WT, the elav-Gal4; Sap47156 driver-control and the UAS-Sap47-RF; Sap47156 effector-control strains show no SAP47 expression; the rescue larvae show an obvious SAP47 band of 47 kDa, as is to be expected from the coding region used for the UAS-Sap47-RF transgene; a higher isoform is only detectable in WT. Anti-SAP47: nc46; anti-CSP: ab49 (loading control). C, Expression of the PF isoform of SAP47 partially rescues impairment in associative function. Associative function is reduced to ∼50% of control level (WT) in genetic controls, using elav-Gal4; Sap47156 as driver- and UAS-Sap47-RF; Sap47156 as effector-strain. Both controls perform equally well and are therefore pooled as genetic controls (supplemental Fig. 8B, available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material). The experimental group shows higher associative performance compared to genetic controls, but does not reach wild-type level. N = 68, 69, 136. Different lettering above plots signifies p < 0.05/2 in Mann–Whitney U tests. The PREF scores underlying all PI values are documented in supplemental Figure 5 (available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material).