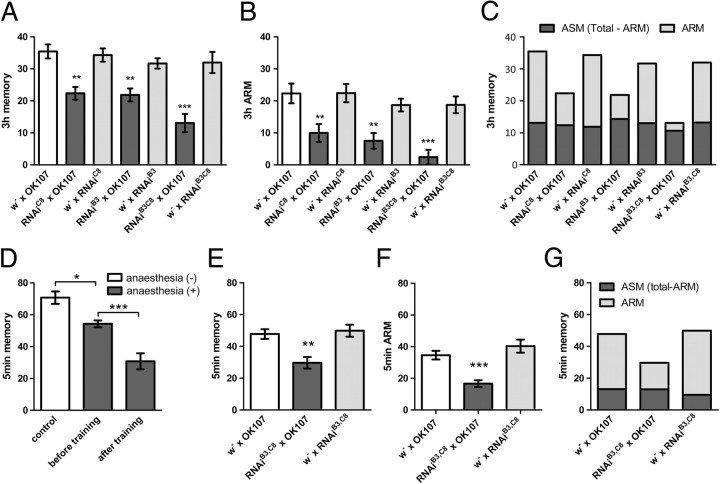
Figure 2.
Bruchpilot is selectively required for ARM. A, brp knockdown in the mushroom body with three different UAS–brp–RNAi lines driven by OK107 leads to a significantly impaired aversive olfactory memory tested at 3 h after training (n = 15–24). B, ARM of the same genotypes. The impairment is similar to that in total 3 h memory that is the sum of ARM and ASM (A) (n = 17–29). C, The score of ASM (calculated by subtracting ARM from total 3 h memory) is similar in all groups (dark gray), whereas ARM is reduced in the experimental groups (light gray). This indicates that ARM is selectively impaired by brp knockdown. Same data as in A and B are represented. D, Five minute memory of wild-type Canton-S flies consists of ASM and ARM (n = 8). Cold anesthesia was applied either before or directly after training. E, brp knockdown with OK107 significantly impairs aversive olfactory STM tested at 5 min after training (n = 13). Cold anesthesia was applied before training (see also D). F, Short-term ARM tested 5 min after training is similarly impaired as the total STM shown in E (n = 13–14). Cold anesthesia was applied directly after training (see also D). G, The score of short-term ASM (calculated by subtracting short-term ARM from the total 5 min memory) is similar in all groups (dark gray), whereas ARM (light gray) is reduced in the experimental group. This indicates that ARM is preferentially impaired by brp knockdown. Same data as in E and F are represented. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; see also Materials and Methods.