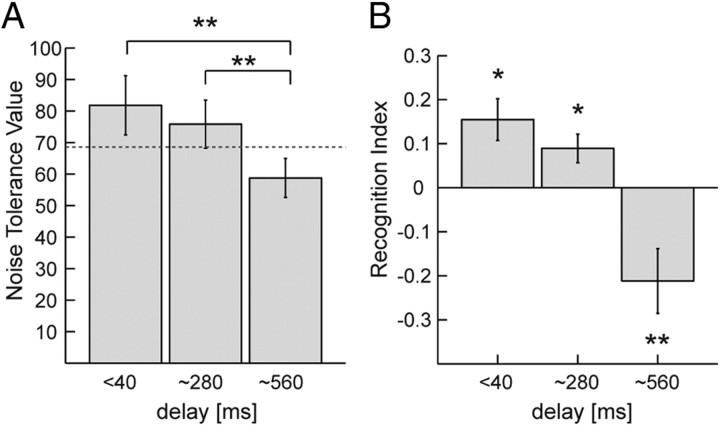
Figure 2.
Influence of time delays on the facilitation of biological motion perception by concurrent motor execution. A, NTV, resulting in 75% correct detections, as function of the temporal delay between the visual stimulus and the executed movements. Error bars indicate SEs. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, significant pairwise differences. The dashed line indicates the noise tolerance value for trials without motor execution (baseline). B, Recognition index computed from the NTVs whose sign indicates facilitation versus interference between visual perception and motor execution. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, significantly different from zero. Error bars indicate SEs.