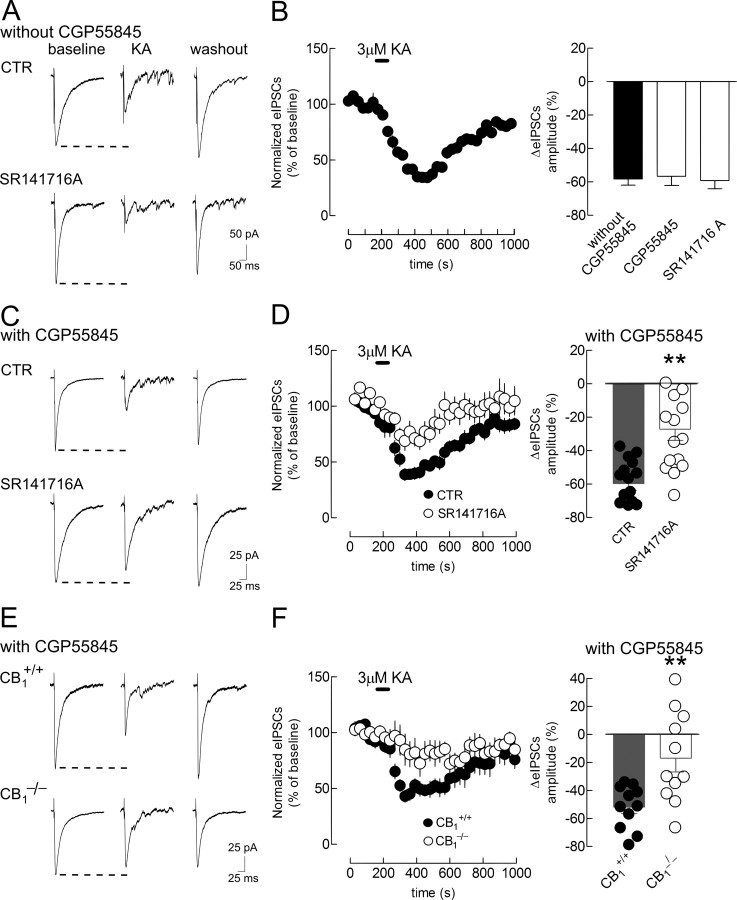
Figure 1.
Inhibition of GABAergic synaptic transmission by KA involves CB1 and GABAB receptors. A, KA depresses eIPSCs in pyramidal neurons from C57BL/6 mice (upper traces, control, CTR), as well as in the presence of the CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716A (5 μm, lower traces). B, Left, Time course of the effect of KA on eIPSC amplitudes in CTR. Right, Bar graph of the maximal effect of KA in CTR conditions (black bar) and in the presence of CGP55845 (5 μm) or in SR141716A-treated slices (see Fig. 3D for time course data). C–F, KA-induced depression of eIPSCs in the presence of CGP55845 (5 μm). C, KA-induced depression of eIPSCs (upper traces, CTR) is reduced by SR141716A (lower traces). D, Left, Time course of the effect of KA on eIPSC amplitudes in CTR and SR141716A-treated slices. Right, Bar graph of the maximal effect of KA in CTR (gray bar, filled circles) and in SR141716A-treated slices (white bar, open circles). E, KA depresses eIPSCs in pyramidal neurons from CB1+/+ (upper traces), but not from CB1−/− mice (lower traces). F, Left, Time course of the effect of KA on eIPSC amplitudes in slices from CB1+/+ and CB1−/− littermates. Right, Bar graph of the maximal effect of KA in slices from CB1+/+ and in CB1−/− mice. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01 (t test).