Figure 2. Fundus of a patient with progressive outer retinal necrosis from VZV infection.
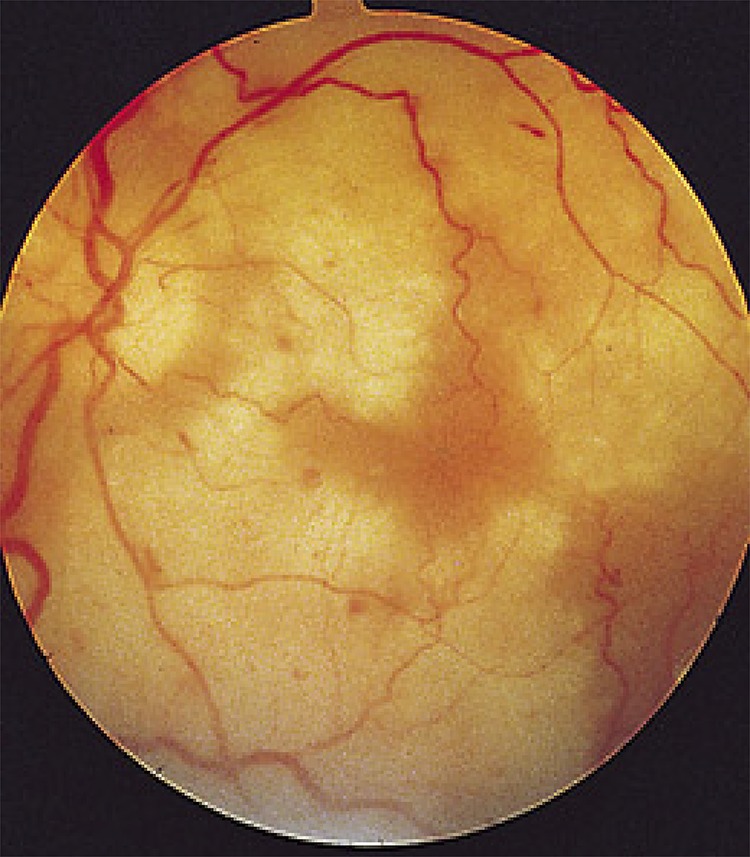
The virus replicates rapidly and spreads through the outer layer of the retina, producing necrotic (white) coalescing lesions and intraretinal hemorrhages. The vitreous typically does not reflect signs of intraocular inflammation, likely due to an immunosuppressed state. Relative preservation of the retinal vasculature also helps to differentiate progressive outer retinal necrosis from retinal artery occlusions. VZV = varicella zoster virus.
