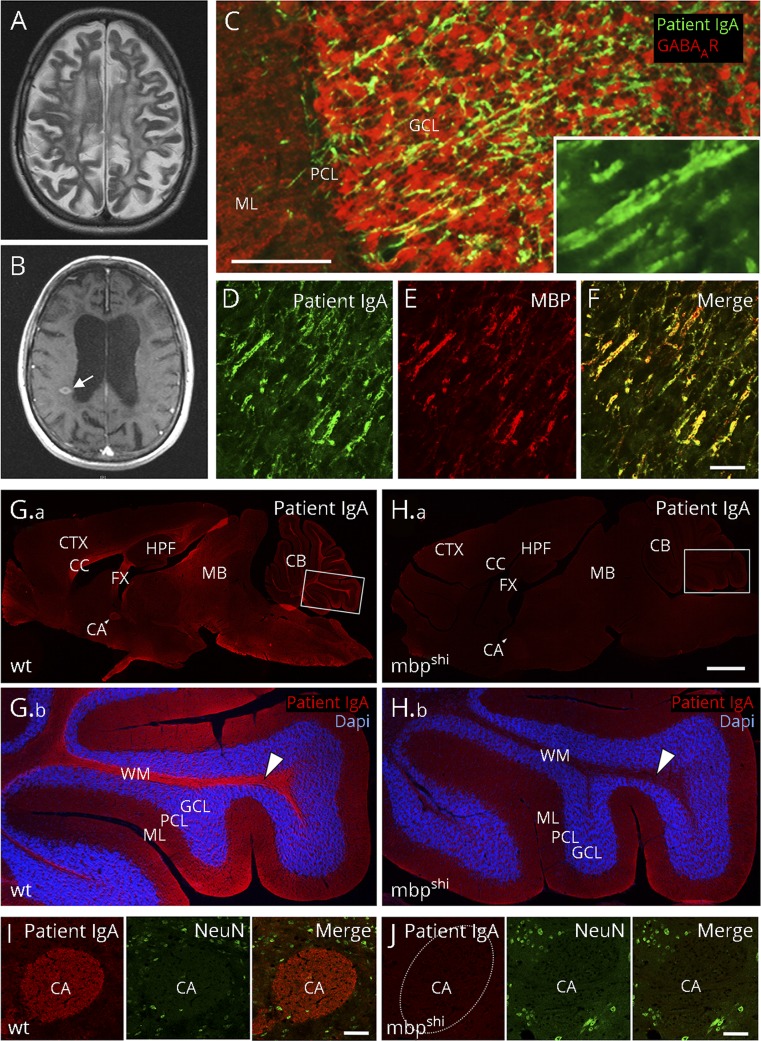
Figure. Myelin binding of high-level MBP IgA antibodies from a patient with MS.
(A) Cerebral MRI shows atrophy, widespread postinflammatory changes and (B) new contrast-enhancing lesions (arrow). (C) Using 20 μm unfixed rat brain sections, patient IgA (4.25 mg/mL, dilution 1:10) labels fine axonal fibers (green, goat anti-human IgA, Dianova, Hamburg, Germany, dilution 1:200) throughout the brain, in particular in the cerebellar cortex (colabeling with a GABAA receptor antibody [red; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA, dilution 1:200] for better anatomical visualization of the cerebellar cortex). (C, inset) Higher magnification shows parallel staining of fibers, indicative of myelin antigens. (D–F) Double-labeling of patient IgA (green) with a commercial anti-MBP antibody [red, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA, dilution 1:200] demonstrates complete overlap in rat cerebellar cortex (merged in [F]). The characteristic immunofluorescence with strong binding to axonal fiber tracts on a 20 µm paraformaldehyde-fixed mouse brain section (G, red) was completely absent in shiverer MBP knockout (mbpshi) littermate mice (H), exemplarily shown at higher magnification in the white matter of the cerebellum (arrowheads in G.b and H.b; double-labeling with DAPI for cell nuclei in blue) or the anterior commissure (I, J; double-labeling with the neuronal marker NeuN in green). Bars represent 50 μm in C–F, 1 mm in G–H and 50 μm in I, J. CA = anterior commissure; CB = cerebellum; CC = corpus callosum; CTX = cortex; FX = fornix; GCL = granule cell layer; HPF = hippocampal formation; MB = midbrain; ML = molecular layer; PCL = Purkinje cell layer; WM = white matter; and wt = wild-type.