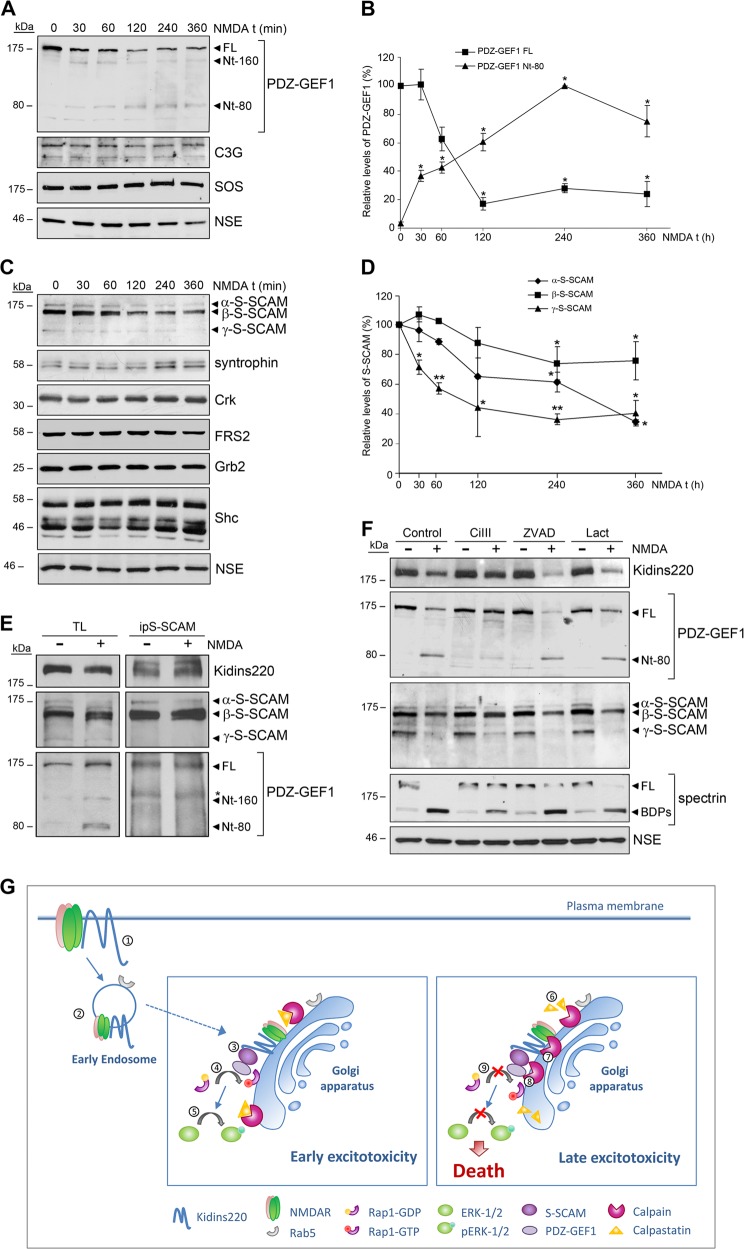
Fig. 8. The components of Rap1 activation complexes S-SCAM and PDZ-GEF1 are downregulated during excitotoxicity by calpain-dependent mechanisms.
a Immunoblot analysis of neuronal cultures stimulated with NMDA for various periods of time using antibodies for PDZ-GEF1 and the indicated proteins. Full-length PDZ-GEF1 (FL) and its derived N-terminal fragments (Nt-160 and Nt-80) are indicated (black arrowheads). b Levels of FL and Nt-80 PDZ-GEF1 were normalized to those of NSE and expressed relative to values found in untreated cells, arbitrary assigned a value of 100% (FL) or 0% (Nt-80). Data represented are the means ± s.e.m. of four independent experiments. *p < 0.05, Student’s t-test. c Immunoblot analysis of neuronal cultures stimulated with NMDA for various periods of time using antibodies for S-SCAM and the indicated proteins. d Quantification of different S-SCAM isoforms levels normalized to those of NSE and expressed relative to values found in untreated cells, arbitrary assigned a value of 100%. Data represented are the means ± s.e.m. of four independent experiments. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01, Student’s t-test. e S-SCAM immunoprecipitation (ip) from untreated or 1 h NMDA-treated neurons performed to detect Kidins220, PDZ-GEF1, and S-SCAM association. The asterisk (*) designates a nonspecific band. f Immunoblot analysis showing the effect of inhibitors specific for calpain (calpain inhibitor III, CiIII, 20 µM), capases (Z-VAD, 100 µM) or the proteasome (lactacystin, Lact, 15 µM) on PDZ-GEF1 and S-SCAM processing induced in excitotoxicity. Neuronal cultures were incubated with protease inhibitors for 1 h before addition of NMDAR co-agonists. Inhibitors were present for the duration of NMDA treatment. Reduced cleavage of the calpain substrate spectrin into breakdown products (BDPs) demonstrates the efficiency of calpain inhibition. g Model of Kidins220 recruitment to the GA and Rap1/ERK activation/inactivation response to excitotoxicity. Kidins220 forms complexes at the neuronal surface with NMDARs (1). At early times of excitotoxicity Kidins220 is targeted to the GA through a Rab5-positive endocytic compartment (2). During this phase, Kidins220 acts as an essential component of Rap1 activation complexes (Kidins220/PDZ-GEF1/S-SCAM) (3), participating in Rap1 activation (4) and the subsequent stimulation of ERK-1/2 (5). At later times of excitotoxicity, the increase in intracellular Ca2+ induced by NMDARs overstimulation could lead to partial activation of Golgi-associated calpain, the cleavage of its inhibitor calpastatin (6), and full enhancement of calpain proteolytic activity. Activated calpain will then process cargos such as Kidins220 (7), and other components of Rap1 activation complexes, PDZ-GEF1 and S-SCAM (8) associated to the GA. Thereby, late excitotoxicity turns off Rap1/ERK cascade (9), thus compromising neuronal survival