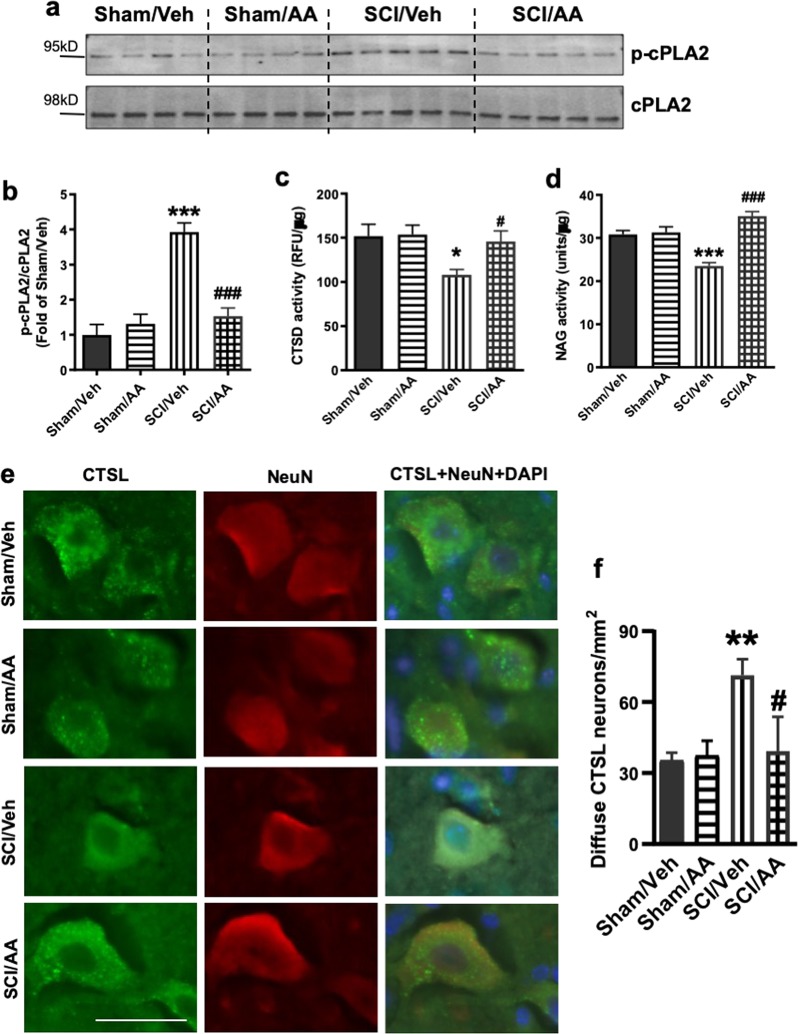
Fig. 6. Inhibition of cPLA2 attenuates SCI-induced lysosomal membrane damage.
a, b Expression of p-cPLA2 and cPLA2 at purified lysosomes from sham control and injured spinal cords at 2 and 24 h. Quantitative analysis of Western blot for the phosphorylation rate of cPLA2 (ratio of p-cPLA2/cPLA2) is indicated in b. N = 4 mice (Sham groups) and 5 mice (SCI groups). c, d Activity of lysosomal enzymes c CTSD and d N-acetyl-glucosaminidase (NAG) is increased in purified lysosomes from the injured spinal cord of mice treated with AACOCF3 (AA). N = 6 mice/group; e, f IHC analysis demonstrating decreased diffused soluble lysosomal enzyme cathepsin L (CTSL, green) in spinal cord ventral horn neurons (NeuN, red) in SCI/AACOCF3 as compared with SCI/vehicle. e Images (20×) of spinal cord sections from Sham/Veh, Sham/AA, SCI/Veh, and SCI/AA mice stained with antibodies against neuronal marker NeuN (red) and CTSL (green). Scale bar = 50 μm. f Corresponding quantification of cells with diffused (cytosolic) CTSL staining. N = 4 (Sham/Veh), 5 (Sham/AA), 7(SCI/Veh), and 4 (SCI/AA). Data are mean ± SEM, Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttests, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus Sham/Veh, #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001 versus SCI/Veh