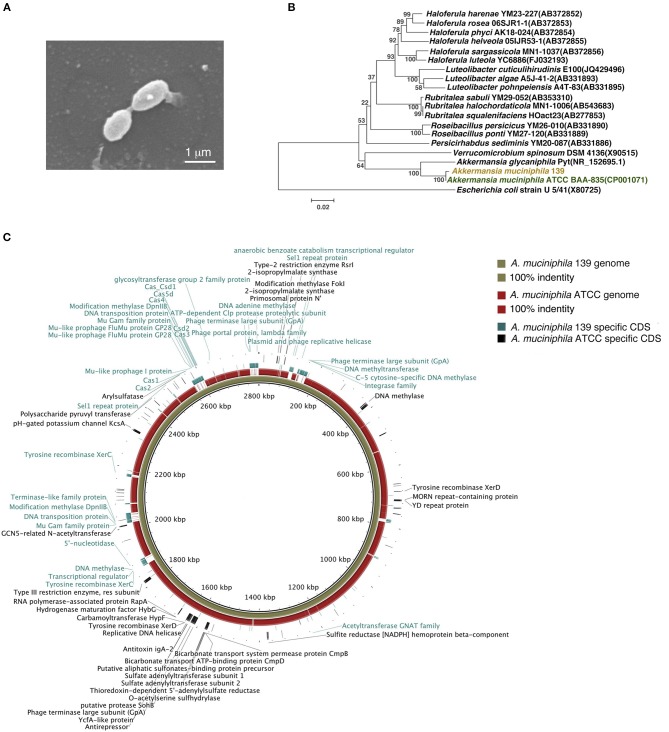
Figure 1.
Identification of murine A. muciniphila strain 139 and its genomic comparison with A. muciniphila strain ATCC. (A) Electron micrograph of strain 139. (B) Phylogenetic relationships of the strain 139 with its relatives based on 16S rRNA gene sequences, and Escherichia coli U5/41 was used as an outgroup. The tree was constructed using the Neighbor-Joining method in MEGA6. The bar indicates sequence divergence. (C) Genomic comparison of the chromosomes of A. muciniphila strain ATCC and 139. Both sequences are started from the predicted replication origin. From inner to outer: (1) contig of strain 139, (2) the identity of genome of strain ATCC blast on the strain 139 based on BLASTN, and (3) the strain-specific CDSs of strain 139 and strain-specific CDSs of strain ATCC. The function of the annotated strain-specific CDSs are also labeled.