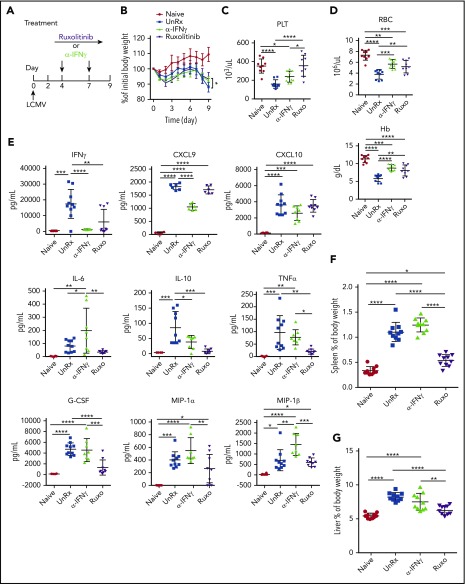
Figure 2.
Ruxolitinib (Ruxo) targets inflammation in a murine model of primary HLH via IFN-γ–dependent and -independent mechanisms. (A) LCMV-infected Prf1−/− mice were left untreated (UnRx) or were treated with αIFN-γ or Ruxo, as shown. On day 9, mice were euthanized and analyzed. Uninfected Prf1−/− mice (Naive) were used as a control. (B) Change in body weight (as a percentage of initial body weight) during the course of the experiment. Body weight percentage was calculated as (actual body weight/ initial body weight) × 100. Peripheral blood samples were analyzed for the number of platelets (PLT) (C) and the number of red blood cells (RBC) and for the levels of hemoglobin (Hb) (D). (E) Levels of serum cytokines were determined using Luminex. (F) Splenomegaly was assessed as a percentage of body weight and calculated as (spleen weight/actual body weight) × 100. (G) Hepatomegaly was assessed as a percentage of overall body weight and was calculated as (liver weight/actual body weight) × 100. Each data point represents 1 mouse. Data were collected from 2 independent experiments and are shown are the mean values ± standard deviation. The total number of mice per group was n = 10 each for Naive, UnRx, αIFN-γ, and Ruxo. For cytokine analysis, the total number of mice per group was n = 6 (Naive), n = 10 (UnRx), n = 8 (αIFN-γ), and n = 9 (Ruxo). Outliers were excluded using Grubb’s test. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, ****P < .0001.