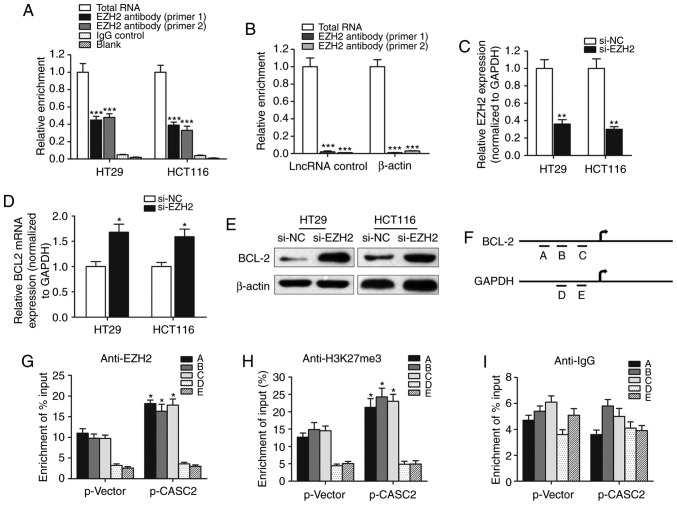
Figure 6.
lncRNA CASC2 decreased the expression level of BCL2 by binding with EZH2. (A) RIP experiments were performed to verify the direct interaction between EZH2 and lncRNA CASC2 by using an anit-EZH2 antibody. Primers used for amplifying CASC2 were generated to verify the enrichment of lncRNA CASC2 pulled down by the anti-EZH2 antibody. ***P<0.001 vs. control IgG group. (B) lncRNA control or β-actin was used as a negative control for CASC2. A RIP assay was performed using EZH2 antibody. ***P<0.001 vs. total RNA group. (C) The silencing effect of siRNA against EZH2 was determined via quantitative PCR. **P<0.01 vs. si-NC group. BCL2 (D) mRNA and (E) protein levels were measured in cells with EZH2 knockdown. *P<0.05 vs. si-NC group. (F) Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis of HT29 cells overexpressing CASC2 was performed with generated primers to detect the amplification at the BCL2 promoter (detection sites A, B and C) and GAPDH promoter (detection sites D and E) regions. Measurement of BCL2 sequences with (G) EZH2, (H) H3K27m3 and (I) IgG is presented as relative to total input. *P<0.05 compared with the p-Vector group, respectively. lncRNA, long non-coding RNA; CASC2, CASC2, cancer susceptibility 2; EZH2, enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit; RIP, RNA immunoprecipitation; siRNA, small interfering RNA; NC, negative control; H3K27m3, H3 lysine 27 trimethylation.