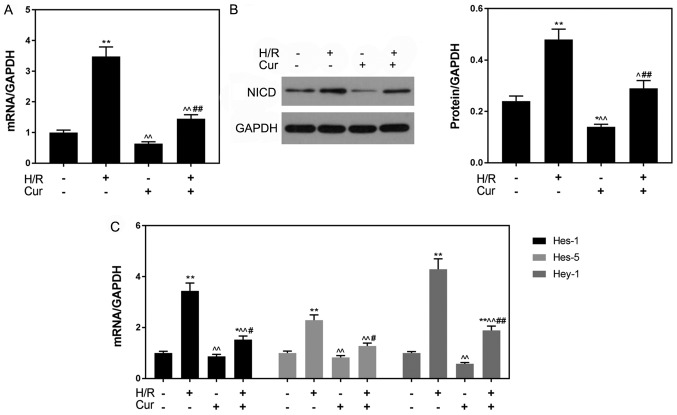
Figure 4.
Curcumin pretreatment inhibits the Notch signaling pathway. (A) mRNA and (B) protein expression levels of NICD as determined via RT-qPCR and western blotting, respectively. (C) Expression of downstream genes (Hes-1, Hes-5 and Hey-1) of the Notch pathway as determined via RT-qPCR analysis. GAPDH was used as an internal control. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. Con; ^P<0.05, ^^P<0.01 vs. H/R; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs. Cur. Con, control (normoxic culture conditions); Cur, curcumin; H/R, hypoxia/reoxygenation; Hes, hairy and enhancer of split; Hey-1, hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif protein 1; NICD, Notch intracellular domain; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.