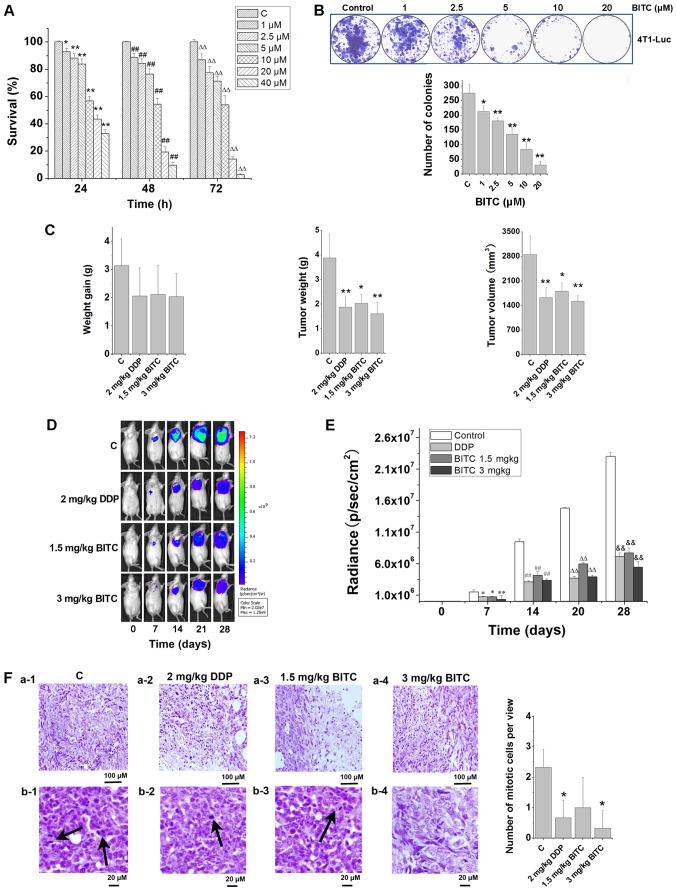
Figure 1.
BITC serves an antitumorigenic role by inhibiting the proliferation and growth of 4T1-Luc cells in vitro and in vivo. (A) BITC inhibited the proliferation of 4T1-Luc cells in a concentration-dependent manner. The viability of 4T1-Luc cells treated with various concentrations of BITC for 24, 48 and 72 h was detected using an MTT assay. N=3/group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. C (24 h); ##P<0.01 vs. C (48 h); ∆∆P<0.01 vs. C (72 h). (B) Clonogenicity of 4T1-Luc cells treated with various concentrations of BITC. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. Control. (C) BITC inhibits the growth of xenograft tumors formed by 4T1-Luc cells in vivo. The antitumorigenic actions of BITC and DDP were detected by measuring (left to right): Weight gain; tumor weight; and tumor volume. N=8/group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. C. (D) Tumors were dynamically detected via bioluminescence in vivo imaging every 7 days (n=8 mice/group). (E) Tumor growth was monitored via bioluminescence in vivo imaging for 4 weeks, and the radiance (p/sec/cm2) detected from the tumors was analyzed. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. Control (7 days); ##P<0.01 vs. Control (14 days); ∆∆P<0.01 vs. Control (21 days); &&P<0.05 vs. Control (28 days). (F) Tumor sections were analyzed via H&E staining. a-1-4, necrosis in control, DDP, 1.5 mg/kg BITC and 3 mg/kg BITC group tissues. b-1-4, mitotic cells in control, DDP, 1.5 mg/kg BITC and 3 mg/kg BITC group tissues (×400). Arrows indicate mitotic cells. *P<0.05 vs. C. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. BITC, benzyl isothiocyanate; C, control; DDP, cisplatin.