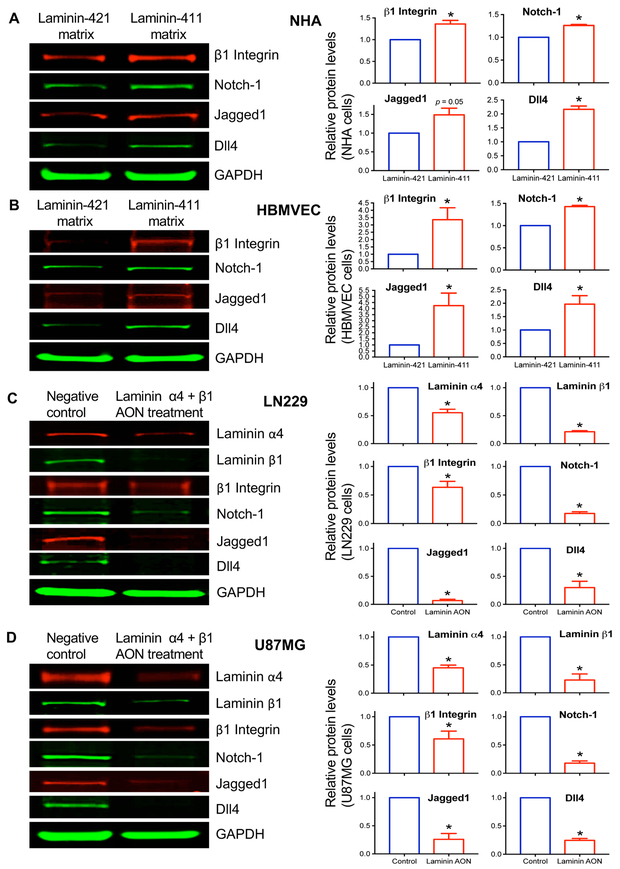
Fig. 5. Upregulation of integrin-Notch pathway by substrate-bound laminin-411 in normal brain astrocytes and endothelial cells and suppression of this pathway in cultured glioma cells by laminin-411 inhibition.
Western blots (left panels) for β1 integrin, Notch-1, Jagged1 and Dll4 expression in A, normal human astrocytes (NHA); and B, human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMVEC) cultured on either laminin-411 (malignant) matrix or laminin-421 (non-malignant) matrix for 3 days. Laminin-411 increased the expression of the integrin-Notch signaling pathway members in both NHA and HBMVEC, as compared with laminin-421. Blot quantitation of expression in NHA and HBMVEC using LI-COR software with the Prism 6 program shows statistically significant differences in marker expression between laminin isoforms. Only Jagged1 in NHA did not reach significance (p = 0.05). Antisense inhibition of laminin-411 α4 and β1 chains in cultured human glioblastoma cell lines C, LN229; and D, U87MG caused downregulation of downstream Notch signaling including β1 integrin, Notch-1, Jagged1 and Dll4. This downregulation was statistically significant. Bar graphs show fold changes (red bars) vs. a control group defined as 1.0. Data are normalized to levels of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) used as a loading control. * p < 0.05 by 2-tailed Student’s t-test.