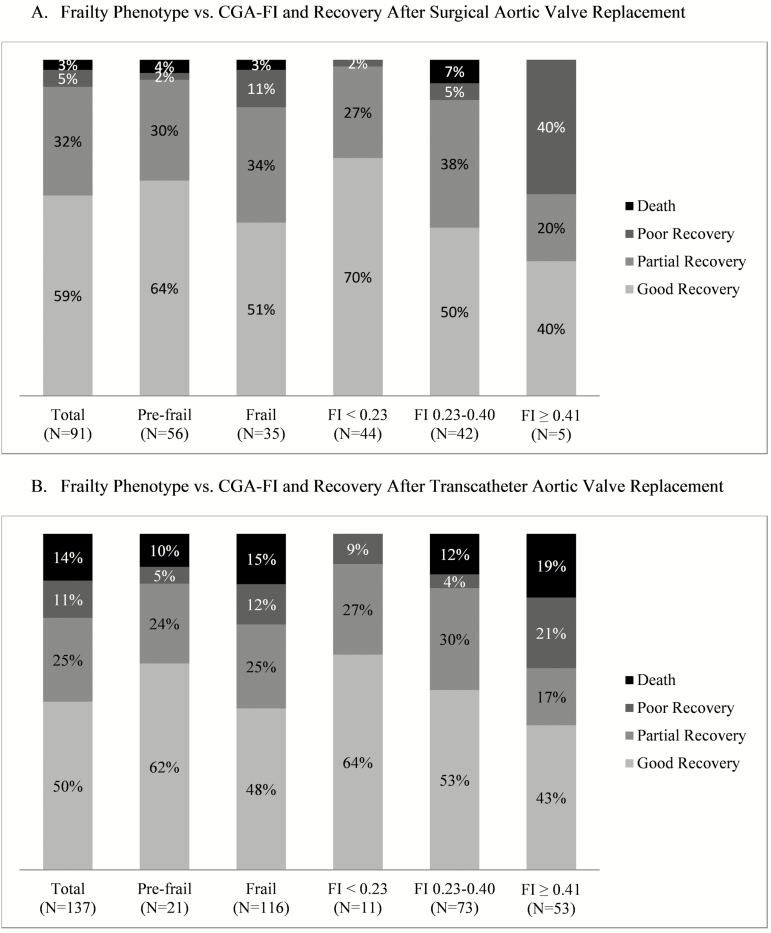
Figure 1.
Frailty phenotype versus frailty index in predicting poor recovery or death after aortic valve replacement. (A) Frailty phenotype versus CGA-FI and recovery after surgical aortic valve replacement. (B) Frailty phenotype versus CGA-FI and recovery after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. CGA-FI, Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment – Frailty Index. Good recovery was defined as alive with functional status same as or improved from baseline; partial recovery was defined as alive with functional status lower than baseline and the New York Heart Association (NYHA) class 1 or 2; poor recovery was defined as being alive with functional status lower than baseline and the NYHA class 3 or 4. There were no robust patients according to the frailty phenotype in the study population.