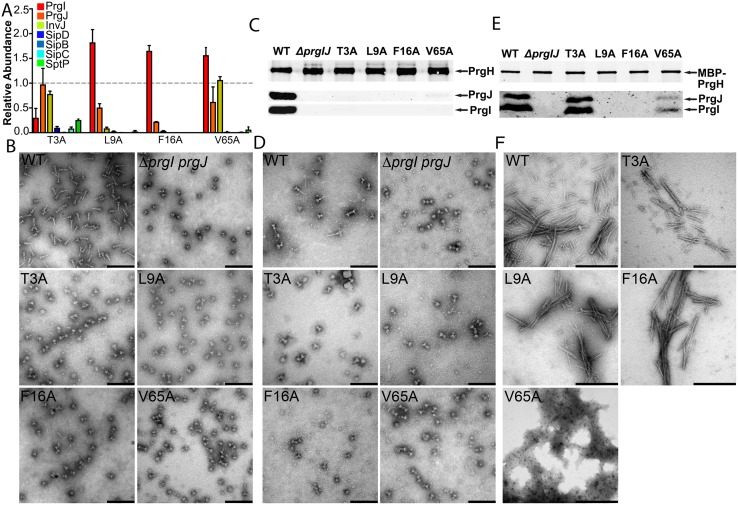
Fig 4. Mutants with an early substrates–only phenotype revealed PrgI determinants for in vivo stability of the needle filament.
(A) Bar graph detailing the secretion phenotypes of S. Typhimurium expressing the indicated PrgI mutants. The relative abundance of the secreted substrates has been standardized relative to WT, which was given a value of 1 and is demarcated by a gray dashed line. All values represent the mean ± the standard deviation of three independent experiments. The data was compiled from the data presented in S2 Fig. The underlying data for this panel can be found in S4 Data. (B–E) Electron micrographs (B and D) and western blot analysis (C and E) of needle complexes isolated by isopycnic ultracentrifugation (B and C) or by affinity purification (D and E). Samples for the western blot analysis were standardized based on the amount of PrgH. Scale bars in B and D: 200 nm; scale bars in E: 500 nm. (F) Electron micrographs of purified recombinant WT PrgI and the T3A, L9A, F16A, and V65A early substrates–only mutants following in vitro polymerization. WT, wild-type.