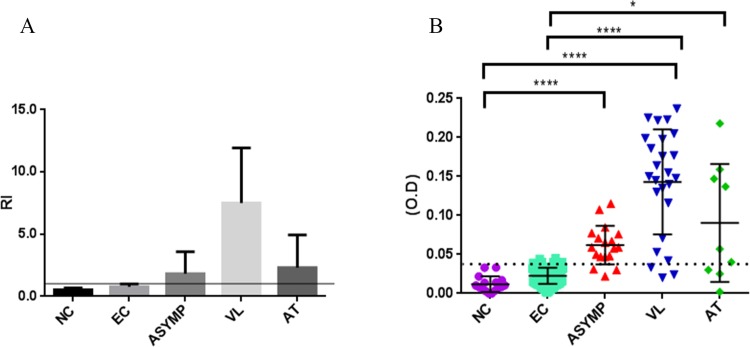
Fig 1. Reactivity indices (RI) and levels of soluble Leishmania antigen (SLA)-specific antibodies in ELISA of serum IgG at a 1:200 dilution of serum for detection of L. infantum-infected asymptomatic individuals.
Fig 1A: Individuals from the endemic area were separated into the following groups according to their RI in ELISA, as described in Marques et al. 2017 [11]: non-infected, endemic control group (EC), characterized by a RI <1.1; asymptomatic infected group (Asymp), active VL group (VL) and individuals who had been treated for VL and were cured (after treatment group, AT), all with a RI ≥1.1. by RI was calculated as follows: mean of optical density each sample divided by the cutoff point of 0.04. Levels of SLA-specific antibodies from healthy individuals from a non-endemic area (normal controls, NC) and EC, Asymp, VL and AT groups as optical density (O.D.) measured at a wavelength of 450 nm. Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's ad hoc test [***, P < 0.0001] (B).