Fig. 3. Mechanical performance and motions of the MXCC/PC bilayer-structured actuator caused by NIR light.
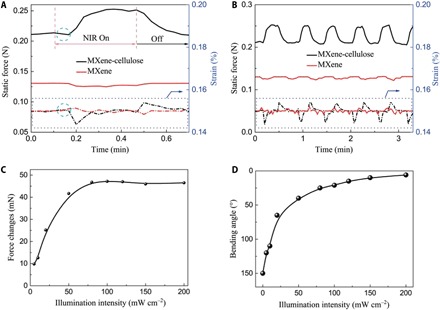
(A) Typical static force and strain changes of the MXCC- and cellulose-based actuators during one actuation cycle when NIR light illumination was turned on and off (50 mW cm−2). (B) Plot of the static force and strain of the MXCC- and cellulose-based actuators as a function of time for five consecutive NIR light on and off cycles, indicating the reversible, stable, and rapid actuation process. (C) Static force changes of the MXCC-based actuator under different NIR illumination intensities (from 5 to 200 mW cm−2). (D) Bending angle of the MXCC-based actuator under different NIR illumination intensities (from 5 to 200 mW cm−2).
