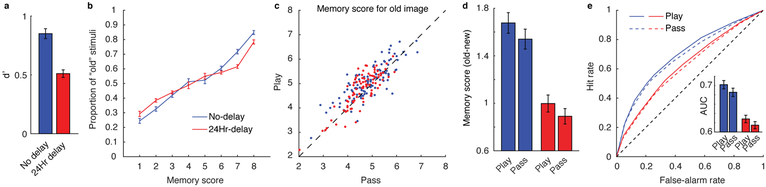
Figure 3.
Dependence of recognition memory strength on gambling behavior. a, Average d’ for the two delay conditions (no delay, N = 109; 24hr delay, N = 90). b, Average proportion of image stimuli that were “old” (presented during the learning task), separated by memory score. c, Mean memory score of “old” images for play vs. pass trials. Each point represents a unique participant. A majority of participants lie above the diagonal, indicating better memory performance for play trials. d, Mean pairwise difference in memory score between the “old” images and their semantically-matched foil images. e, ROC curves for play vs. pass trials. Area under the ROC curves (AUC) is shown in the inset. AUC was greater for play versus pass trials, indicating better detection of old vs. new images for play trials compared to pass trials. Error bars indicate standard error across participants. Colors indicate time between encoding and memory testing; blue = no delay, red = 24 hour delay.