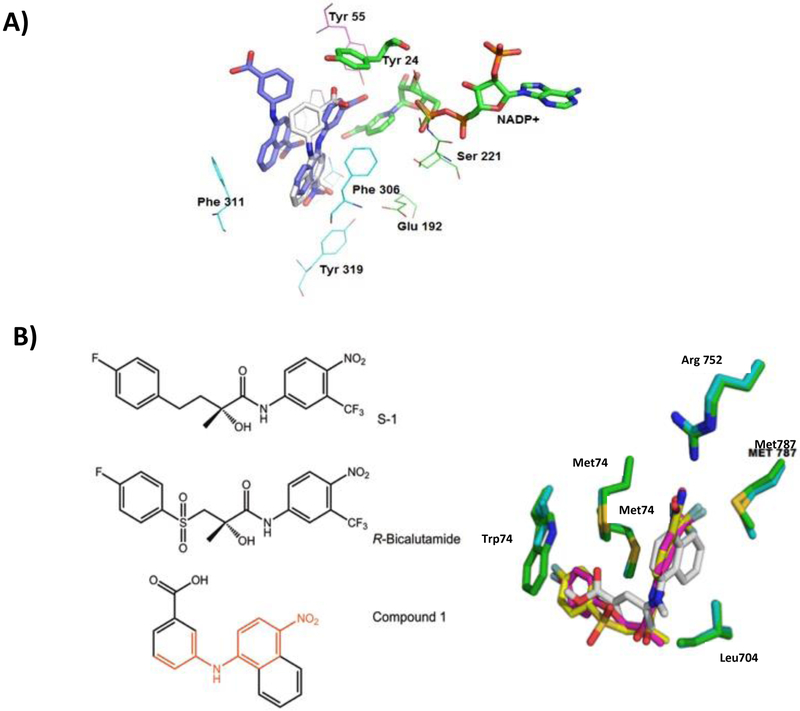
Figure 11.
Molecular Modeling Experiments: Binding to AKR1C3 and AR. Predicted binding poses for Compound 4 in the AKR1C3 active site. AKR1C3 subpocket 1 (cyan), AKR1C3 subpocket 3 (green), Compound 1 (purple), Compound 4 (white), oxyanion site (residues highlighted in magenta). The structures are based on the crystal structure of the AKR1C3•NADP+ and 3’-[4-nitronaphthalen-1-yl)amino]benzoic acid complexes (PDB code: 4DBS), (A). Comparison of the binding of compound 1 in the AR-LBD site to S-1 and R-bicalutamide in AR-LBD and AR-LBD W741L (B). Left panel, red bonds in compound 1 shows similarity with the AR ligands. Right panel, AR-LBD (green), nonsteroidal agonist modulator S-1 (magenta), AR-LBD W741L (cyan), R-bicalutamide (yellow) and compound 1 (white). Structures of AR-LBD W741L in complex with R-bicalutamide (1Z95) The figure was generated with Pymol (Delano Scientific).