Table 1.
Anti-BCSCs effects of food-derived polyphenols.
| Compound | Polyphenol concentration | Effects on CSCs | Molecular targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
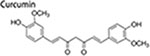 |
15 μM | inhibit migration, invasion and EMT |
a↑E-cadherin/β-catenin complex; ↓nuclear β-catenin; b↑epithelial markers (E-cadherin, cytokeratin-18 and -19); ↓β-catenin transcriptional targets (cyclin D1, c-Myc, and Slug); ↓EMT-promoting factors (vimentin, MMP-2 and MMP-9) |
(Mukherjee et al., 2014) |
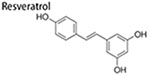 |
10–40 μM 100 mg/kg/d |
inhibit mammosphere formation; induce autophagy; inhibit tumor growth in vivo; inhibit ALDH + BCSCs tumorigenicity in vivo | ↓β-catenin and cyclin D1 ↑LC3-II, Beclin1 and Atg7 |
(Fu et al. 2014) |
| 50 μM 25 mg/kg/d |
reduce invasive ability inhibit tumor growth | ↑miR-16, -141, -143, and -200c ↑Argonaute2 (Ago2) ↓Zeb1 ↑E-cadherin |
(Hagiwara et al. 2012) | |
| 50-100 μM 22.4 kg/body weight |
reduce mammosphere formation; reduce breast cancer cells viability; induce BCSCs apoptosis; inhibit tumor growth in vivo suppress lipid syntheses | ↓fatty acid synthase ↑pro-apoptotic genes (DAPK2, BNIP3) |
(Pandey et al. 2011) | |
| 50-100 μM | decrease BCSCs proliferation; induce BCSCs apoptosis; down-regulate lipogenesis; inhibit mammosphere formation; | ↓SREBP1 ↑pro-apoptotic genes (DAPK2, BNIP3) ↓SREBP1 downstream genes (ACLY, ACC1 and FAS) | (Pandey et al. 2013) | |
| 25,50 μM | attenuate migrational and invasive ability decrease proportion of BCSCs inhibit mammosphere formation | ↓Cyclin D1and c-Myc ↓MMP-2 and -9 ↓Sox-2 and CD44 ↓p-Akt and p-Stat3 |
(Suh, Kim, and Surh 2018) | |
| Resveratrol analog HS-1793 | 0.6–2.5 μM 1.5 mg/kg |
reduce invasive ability enhance radiosensitivity and apoptosis induced by radiotherapy | ↓Oct4, KLF4 and Sox2 protein ↓VEGF ↓HIF-1α |
(Choi et al. 2016) |
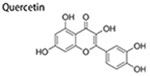 |
12.5–50 μM | inhibit size and number of mammo-spheres; decrease population of ALDH + cells; suppress EMT and migration; | ↓Hsp27 ↓N-cadherin and twist ↑E-cadherin |
(Li et al. 2011) |
| 12.5-50 μM | repress BCSCs inhibit tumor growth inhibit VM capability | ↓Hsp27 | (Lee et al. 2014) | |
| 20 μM | inhibition migration and population of ALDH + cells | ↓Hsp27 | (Lee et al. 2012) | |
| 0.7 μM | decrease population of CD44+/CD24− cells improve chemosensitivity | ↓nuclear Y-box binding protein 1 ↓P-glycoprotein |
(Li, Zhao, Wang, Yuan, et al. 2018) | |
| 50 μM | decrease population of CD44+/CD24− cells inhibit mammosphere formation inhibit tumor growth | ↓PI3K/Akt/mTOR | (Li, Zhou, Wang, Liu, et al. 2018) | |
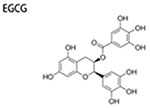 |
10-40 μM | inhibit mammosphere formation; inhibit CD44+/CD24− cells | ↓ER-α36 ↓EGFR |
(Pan et al. 2016) |
| 20–160 μg/mL 16.5 mg/kg |
induce apoptosis of the ALDH + SUM-149 cells; inhibit mammosphere formation; inhibit tumor growth in xenograft mouse model | ↓lymphangiogenesis-promoting genes ↓VEGF-D |
(Mineva et al. 2013) | |
| EGCG analogs | 10,20 μM | inhibit mammosphere formation; inhibition CD44+ high/CD24− low cells | (Chen et al. 2012) | |
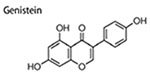 |
0-30 μM 0–50 mg/kg |
inhibit mammosphere formation; decrease ALDH + levels in xenograft tumors; decrease CD44+CD24− population; | ↓Smo ↓Gli1 |
(Fan et al. 2013) |
| 2 μM, and 40 nM | induce differentiation of BCSCs; decrease CD44+/CD24−/ESA+ cells; | ↑differentiated cell markers (E-cadherin, α-smooth muscle actin and Claudin-1 genes) ↓stem cell markers (Fibronectin and Snail); ↑ phospho-Akt308/473 ↑ phospho-ERK1/2 ↑Amphiregulin ↑phospho-β-catenin |
(Liu et al. 2016) | |
| 2 μM, and 40 nM | inhibit adipogenesis inhibit mammosphere formation; | ↑mammary tumor suppressor (PTEN and E-cadherin) ↓Pparγ ↓fatty acid synthase ↑estrogen receptor b |
(Montales et al. 2013) | |
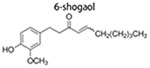 |
2 μM, and 40 nM 1–40 μM |
inhibit mammosphere formation inhibit primary and secondary mammo-sphere formation; decrease CD44+/CD24− cells proportion; |
↑PTEN ↓Cleaved Notch1 ↓Hes1 and Cyclin D1 |
(Montales et al. 2012) (Ray, Vasudevan, and Sengupta 2015) |
| 5-25 μM | inhibit mammosphere formation; decrease CD44 expression of BCSCs; increase chemosensitivity of BCSCs; induce cell necrosis phenomena; | ↓hedgehog ↑p-β-catenin ↓CD44 ↓c-Myc ↓cyclin D1 |
(Wu, Hong, et al. 2015) | |
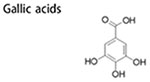 |
– | inhibit metastasis; inhibit tumor growth; inhibit mammosphere formation; suppress cell migration and mobility | ↓PI3K/AKT signaling ↓MAPK/ERK signaling ↓STAT3 signaling |
(Vuong et al. 2016) |
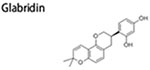 |
10 μM 20 mg/kg Body Weight |
decrease mesenchymal features; inhibit mammosphere formation; inhibit tumor growth; | ↓TGFβ-SMADs Signal ↑miR-148a ↓DNMT1 and DNMT3a |
(Jiang et al. 2016) |
 |
25, 50 μM 50 mg/kg/d |
inhibit self-renewal and multi-differentiation; reduce BCSCs proportion; inhibit tumor growth; | ↓heat shock 70kDa protein 5 ↓β-catenin/ABCG2 signaling |
(Wang Wang, et al. 2014) |
| 25, 50 μM 50 mg/kg/d |
block self-renewal BCSCs; reduce BCSCs population; induce BCSCs G0/G1 phase arrest; inhibit tumor growth; | ↓DNMT1 methyltransferase ↑WIF1 ↓β-catenin signaling |
(Wang Wang, et al. 2015) | |
| Curcumin + piperine | 5,10 μM | inhibit mammosphere formation; reduce the percent of cells bearing ALDH1+ | ↓Wnt signaling | (Kakarala et al. 2010) |
| Curcumin + Mitomycin C | 5–40 μM 100 mg/kg |
nhibit mammosphere formation; reduce cells expressing CD44+CD24−/low; inhibit tumor growth in vivo | ↓ABCG2 and ABCC1 | (Zhou et al. 2015) |
| Curcumin + EGCG | 10 μM, 10 μM | inhibit mammosphere formation; inhibit invasion; reduce CD44−expressing subpopulation | ↓p-STAT3 ↓nuclear STAT3-NFkB |
(Chung Seyung 2015) |
↓Represents down-regulation;
↑Represents down-regulation.
Abbreviations: ACC1, acetyl CoA carboxylase 1; ALDH, aldehyde dehydrogenase; ACLY, ATP-citrate lyase; BCSCs, breast cancer stem cells; EMT, epithelial mesenchymal transition; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ER-α36, estrogen receptor-α36; FAS, fatty acid synthase; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; Hsp, Heat shock protein; MMP, metal matrix proteinase; PPARγ, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; SREBP1, sterol regulatory element binding proteins1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
