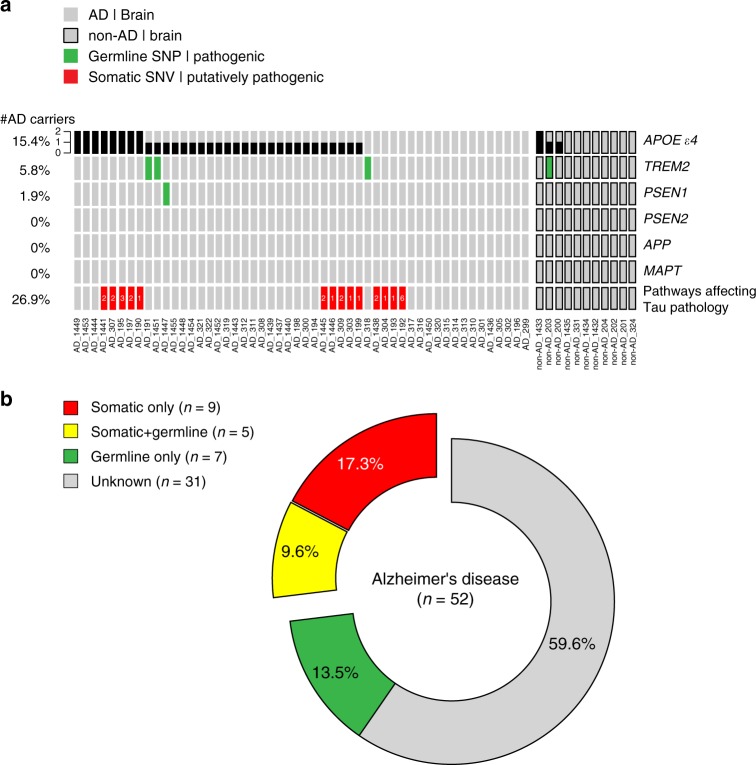
Fig. 4.
Landscape of pathogenic germline and somatic mutations contributing to Alzheimer’s disease (AD). a The presence of pathogenic germline risk factors and putatively pathogenic somatic mutations across all AD and non-AD individuals. The copy number of APOE ɛ4 alleles are annotated in black. Known risk modifiers of AD in APP, PSEN1/2, TREM2, and MAPT are marked in green. Putatively pathogenic brain somatic mutations associated with tau hyperphosphorylation-related pathways are marked in red, and the number of affected genes was annotated together. b Categorization of pathogenic germline and somatic mutation carriers among AD patients. 13.5% (7/52) of AD patients in our cohort could be explained by germline mutations alone; 26.9% (14/52) of AD patients harbored putatively pathogenic somatic mutation affecting the phosphorylation of tau